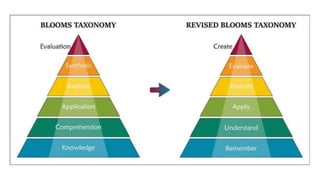
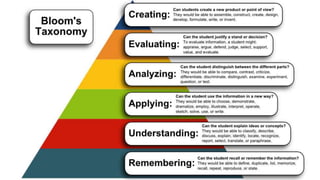
This document discusses teaching methodology and the elements of an instructional system. It outlines 10 key elements: specifying objectives, selecting content, assessing student entry behavior, learning strategies, classroom organization, allocating time, allocating learning spaces, selecting resources, evaluating performance, and providing feedback. The role of the teacher is also discussed, including being the designer of the instruction program, having subject matter expertise, writing objectives, choosing resources and techniques creatively, and assessing/evaluating teaching.