Radioisotopes are unstable isotopes that decay and emit radiation. They are used for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes. Some important radioisotopes include carbon-14, hydrogen-3, iodine-125, and iodine-131. Radioimmunoassay is an analytical technique that uses the principles of radioactivity and antibody-antigen reactions to detect substances in biological fluids at very low concentrations. It has applications in measuring hormones, vitamins, and diagnostic markers. While radioisotopes are useful tools, their use also requires safety precautions due to associated radiation hazards.










![7. Positron emission tomography scan. In this technique2-
[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose(FDG) is used as a molecular probe
which is taken up by all cells and gets phosphorylated to FDG-6-
Phosphate by hexokinase. Cells accumulate FDG as per the rate
of glycolysis. Tumour cells accumulate more FDG since they have
higher rate of glycolysis and detected by PET Scan.
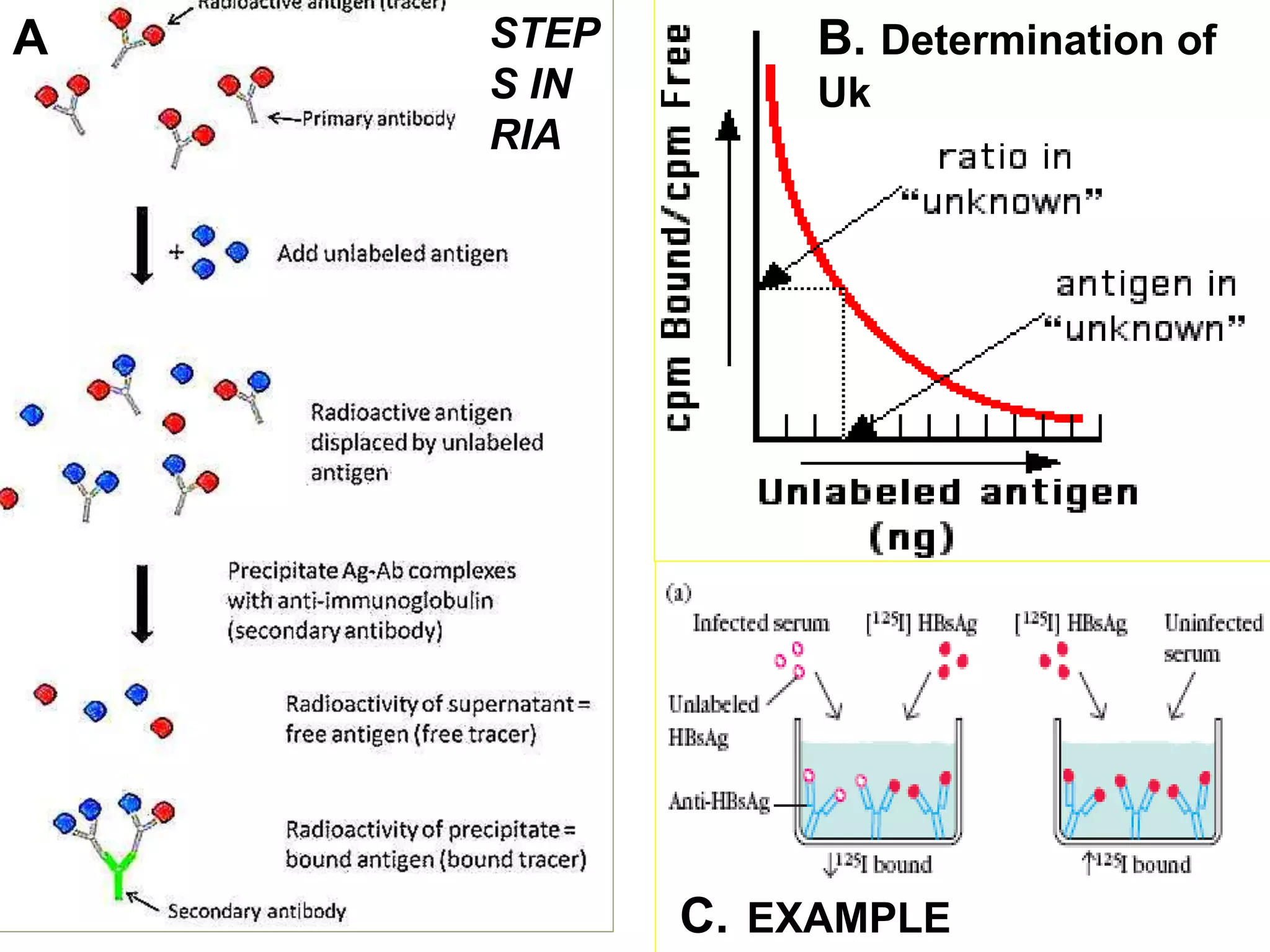
8. Radioimmuno assay (RIA): Assays using 125I labelled
antigens are used to quantitate hormones, tumor markers and
other biological substances present in blood in very small
quantities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radioisotopes-jps-151221170647/75/Radioisotopes-jps-11-2048.jpg)