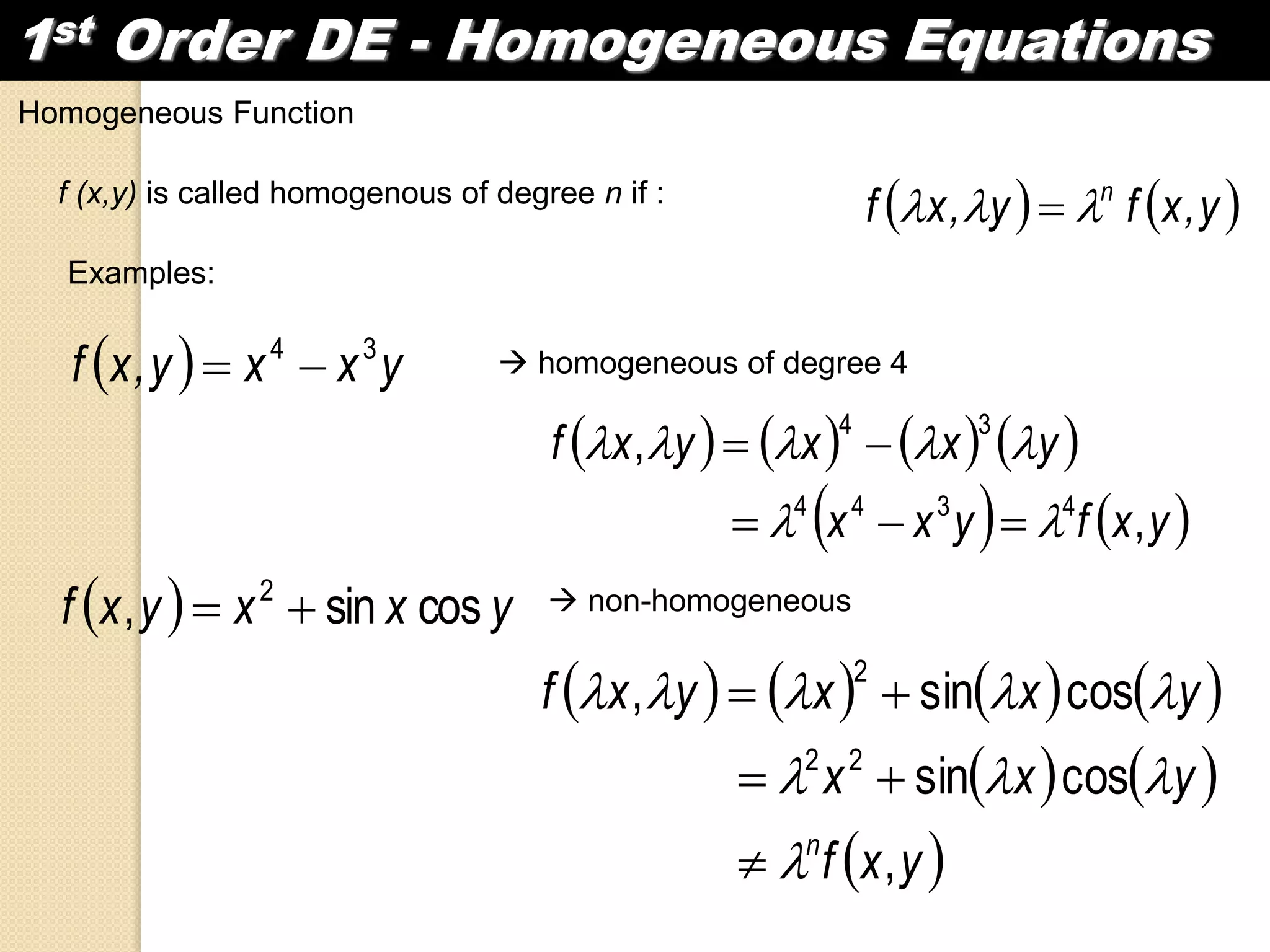
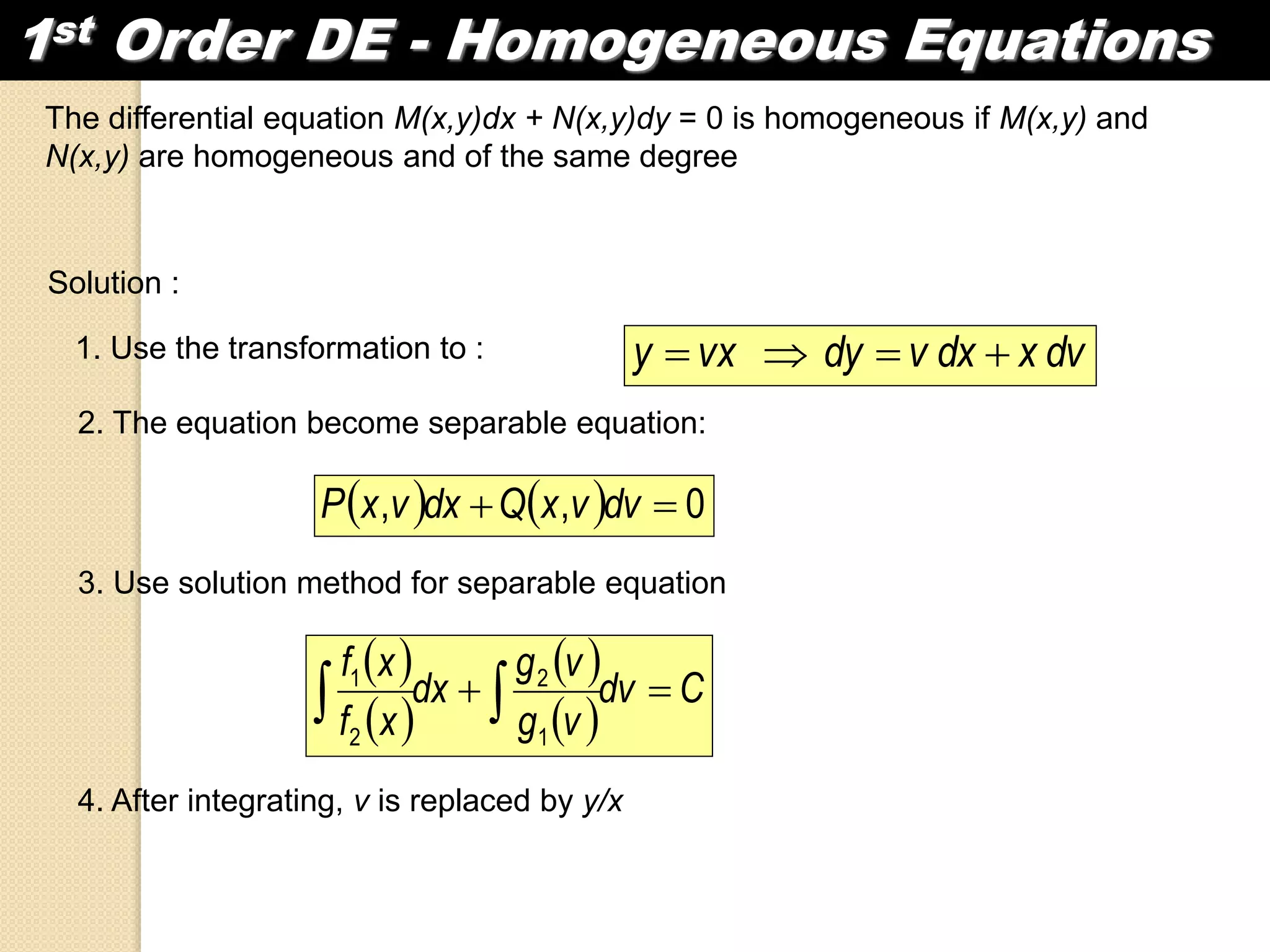
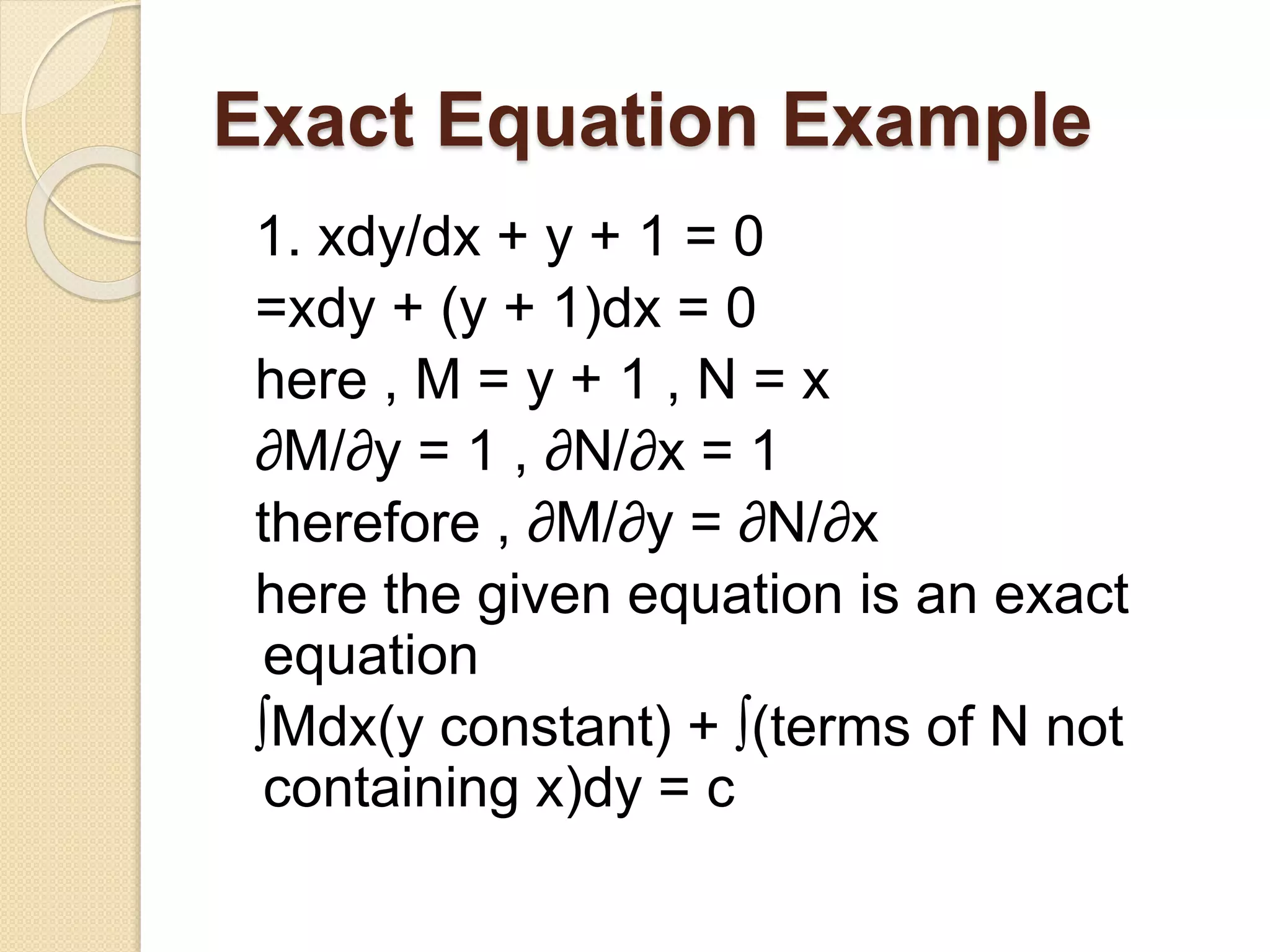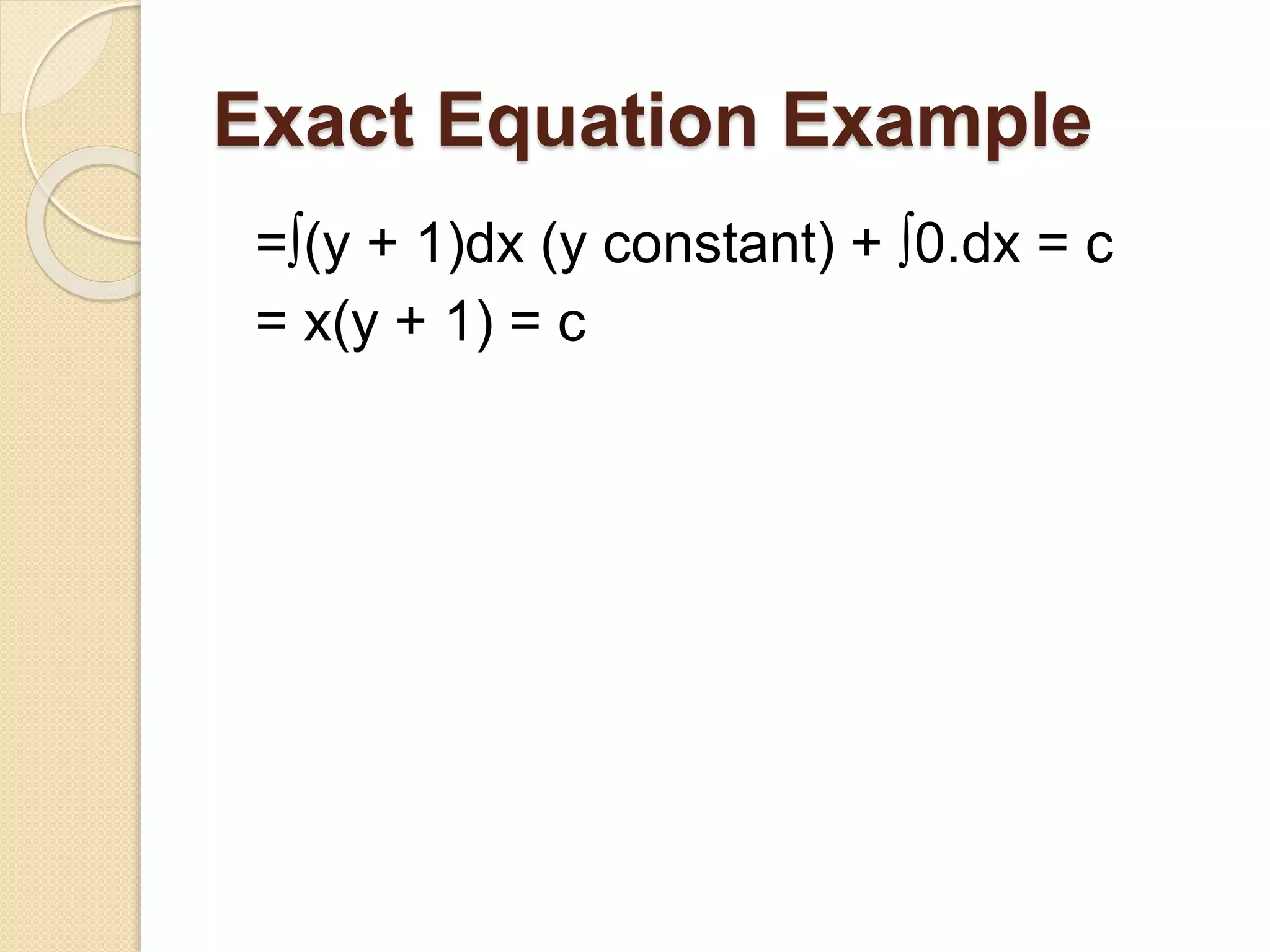1) A differential equation contains an independent variable (x), a dependent variable (y), and the derivative of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable (dy/dx).
2) The order of a differential equation refers to the highest order derivative present. For example, an equation containing dy/dx would be first order, while one containing d2y/dx2 would be second order.
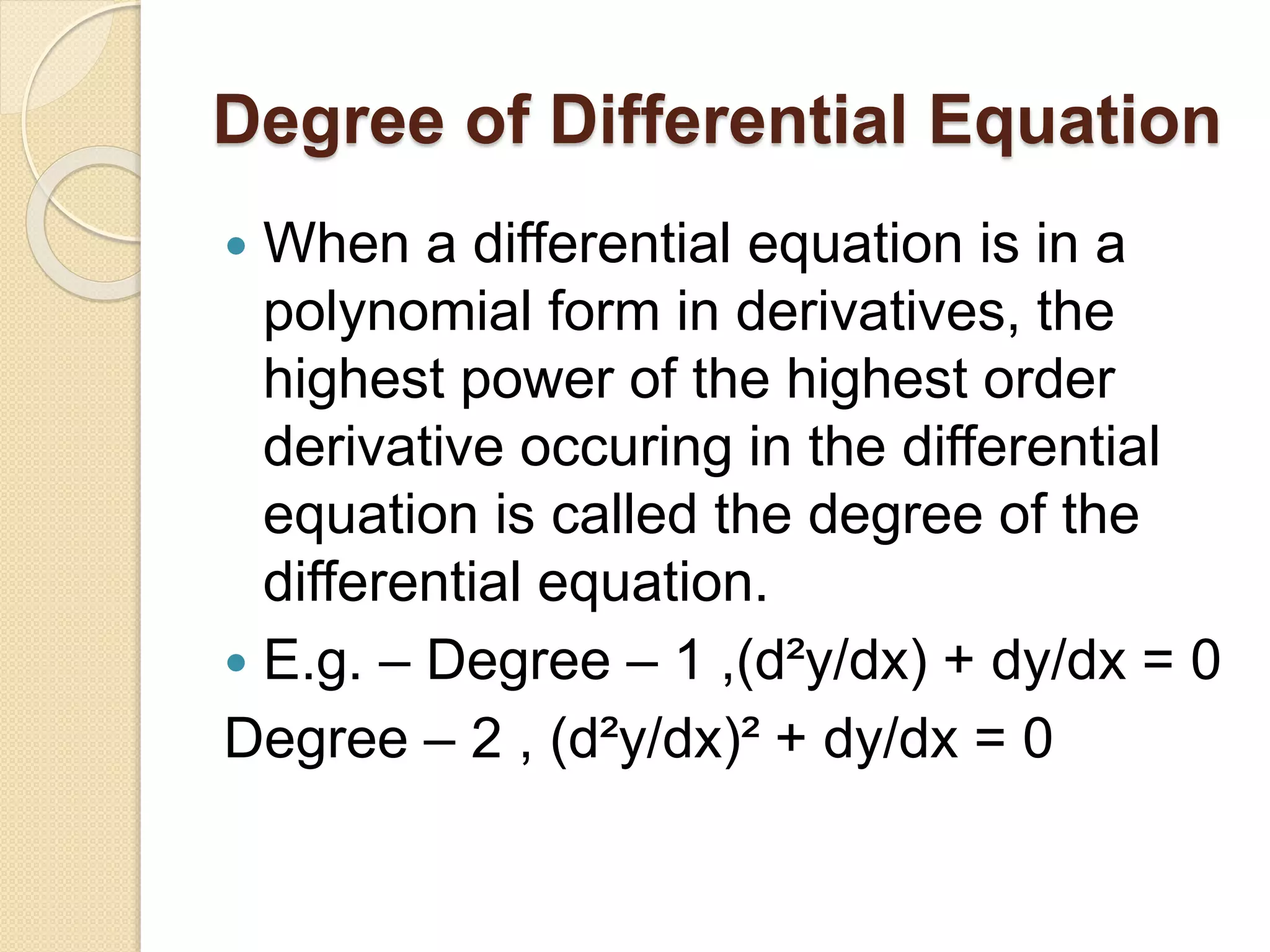
3) The degree of a differential equation refers to the highest power of the highest order derivative. For example, an equation containing (d2y/dx) would be degree 1, while one containing (d2y/dx)2 would be degree 2.
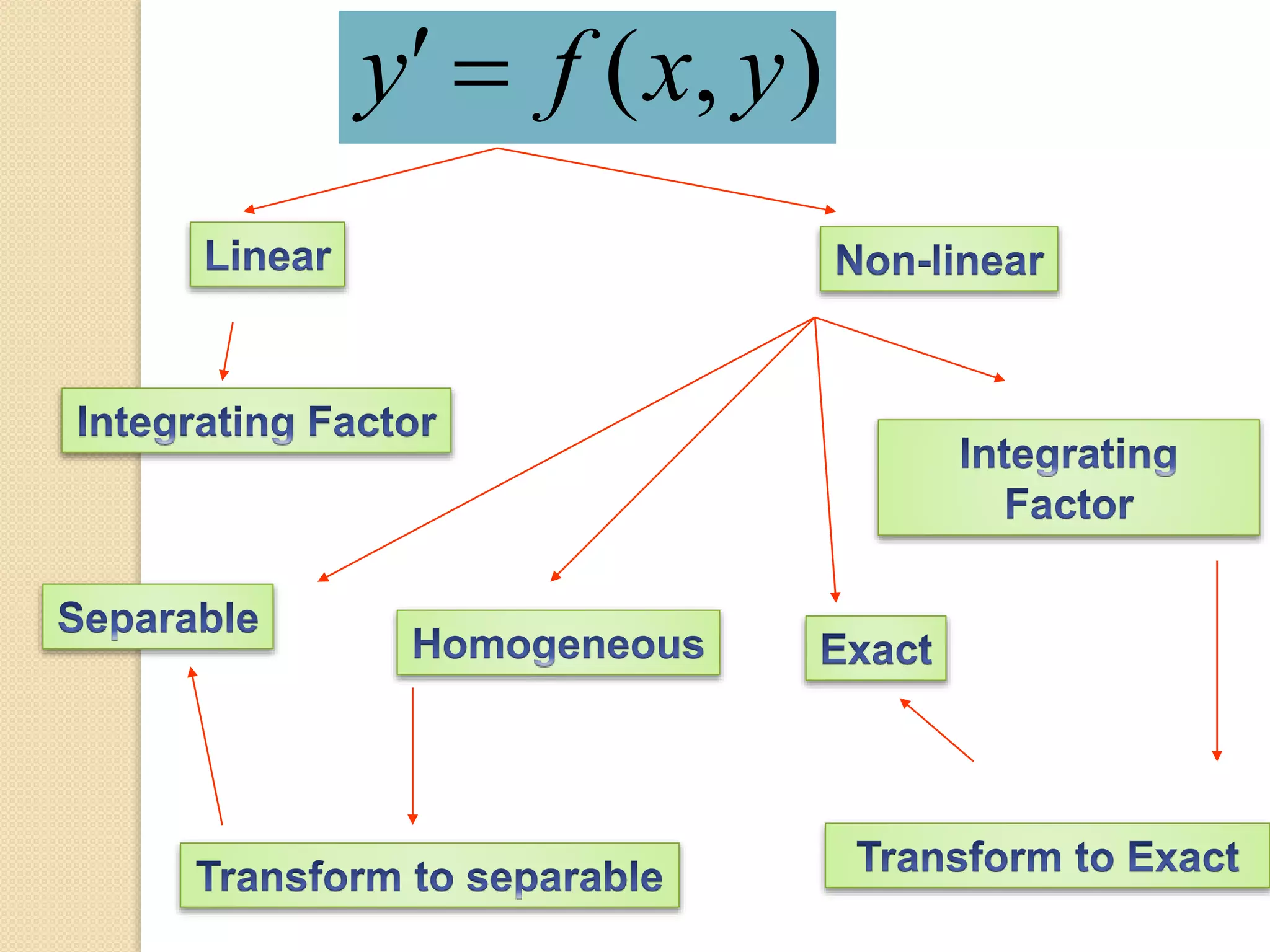
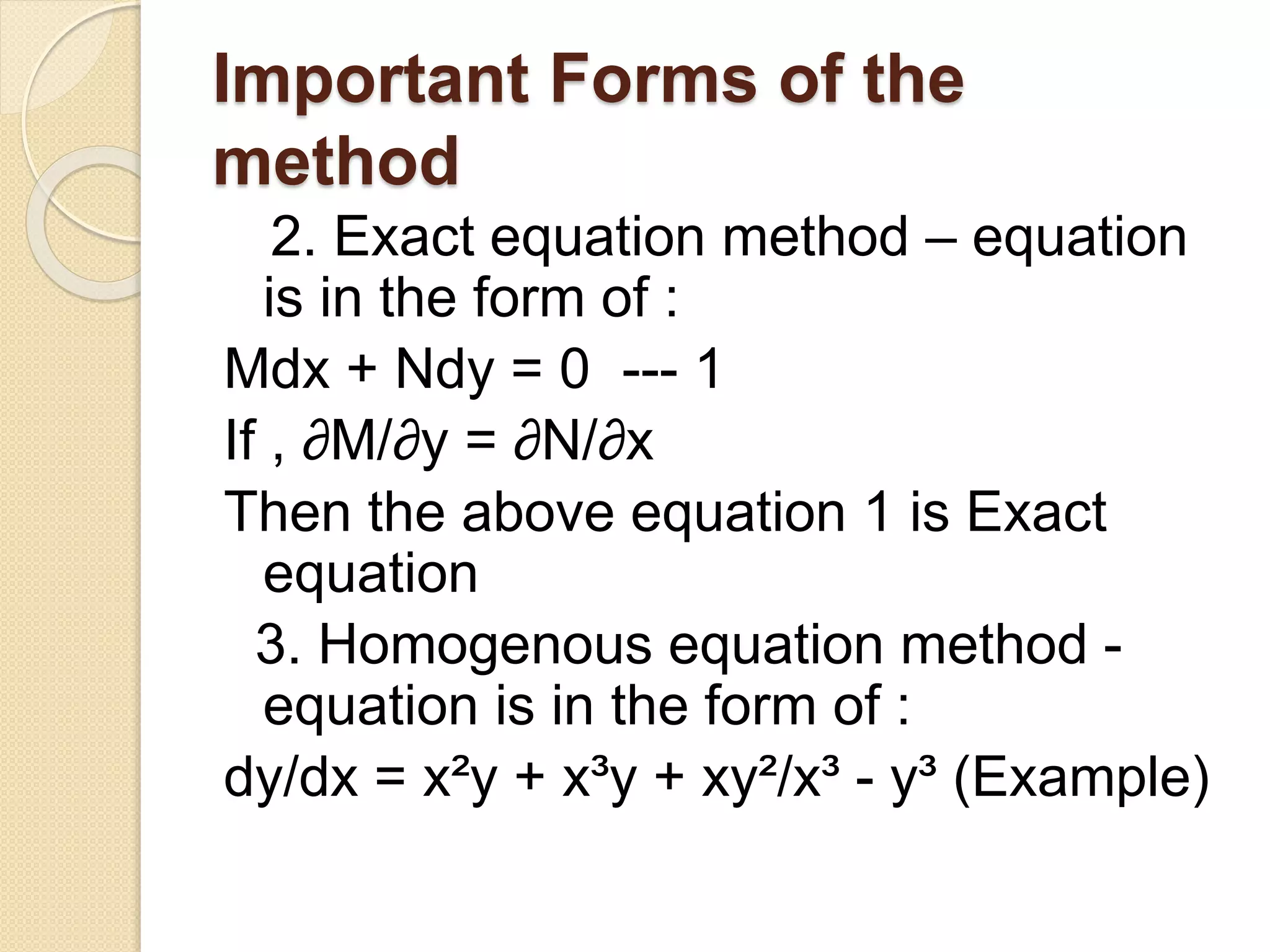
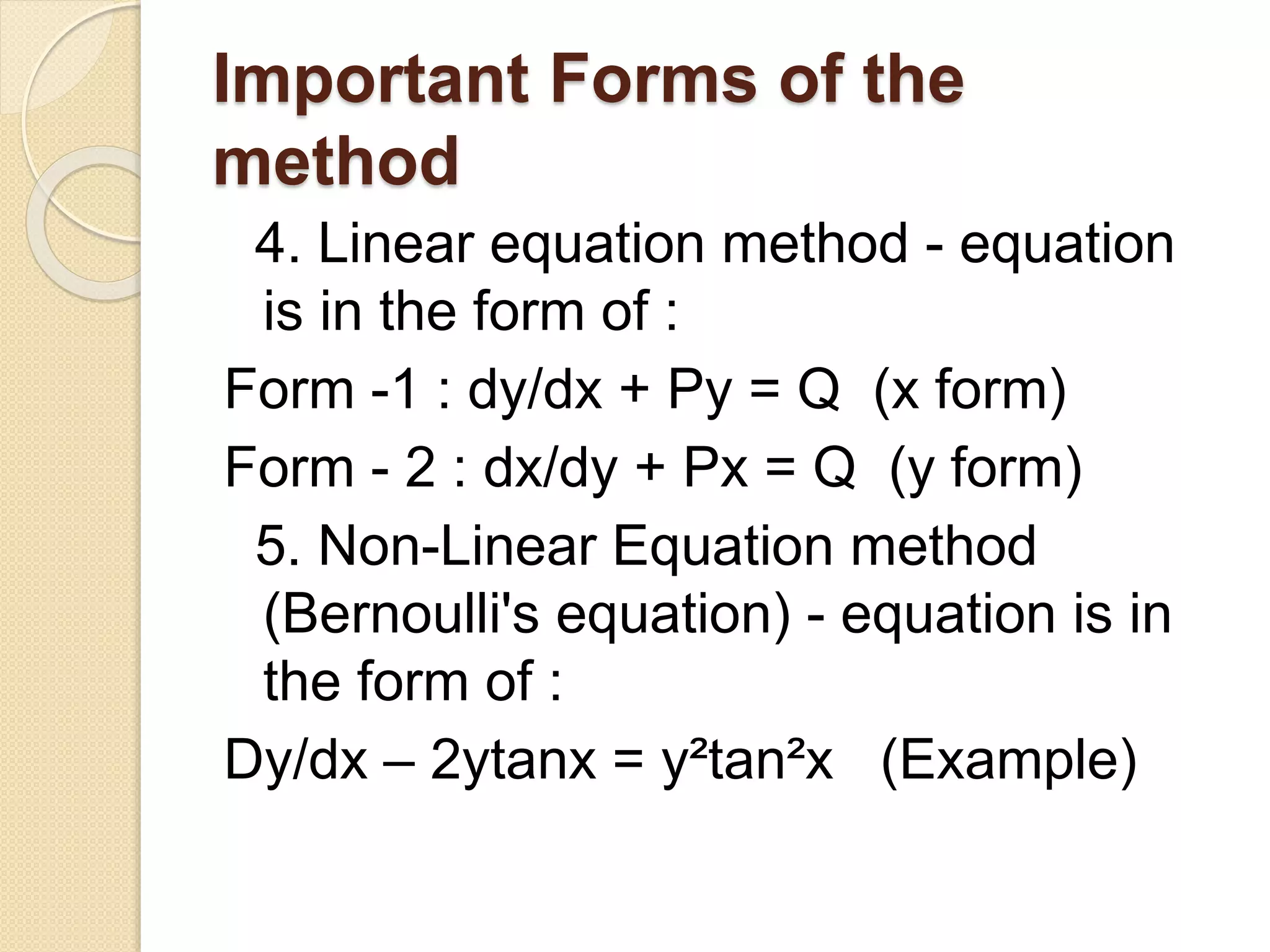
4) There are several methods for solving first