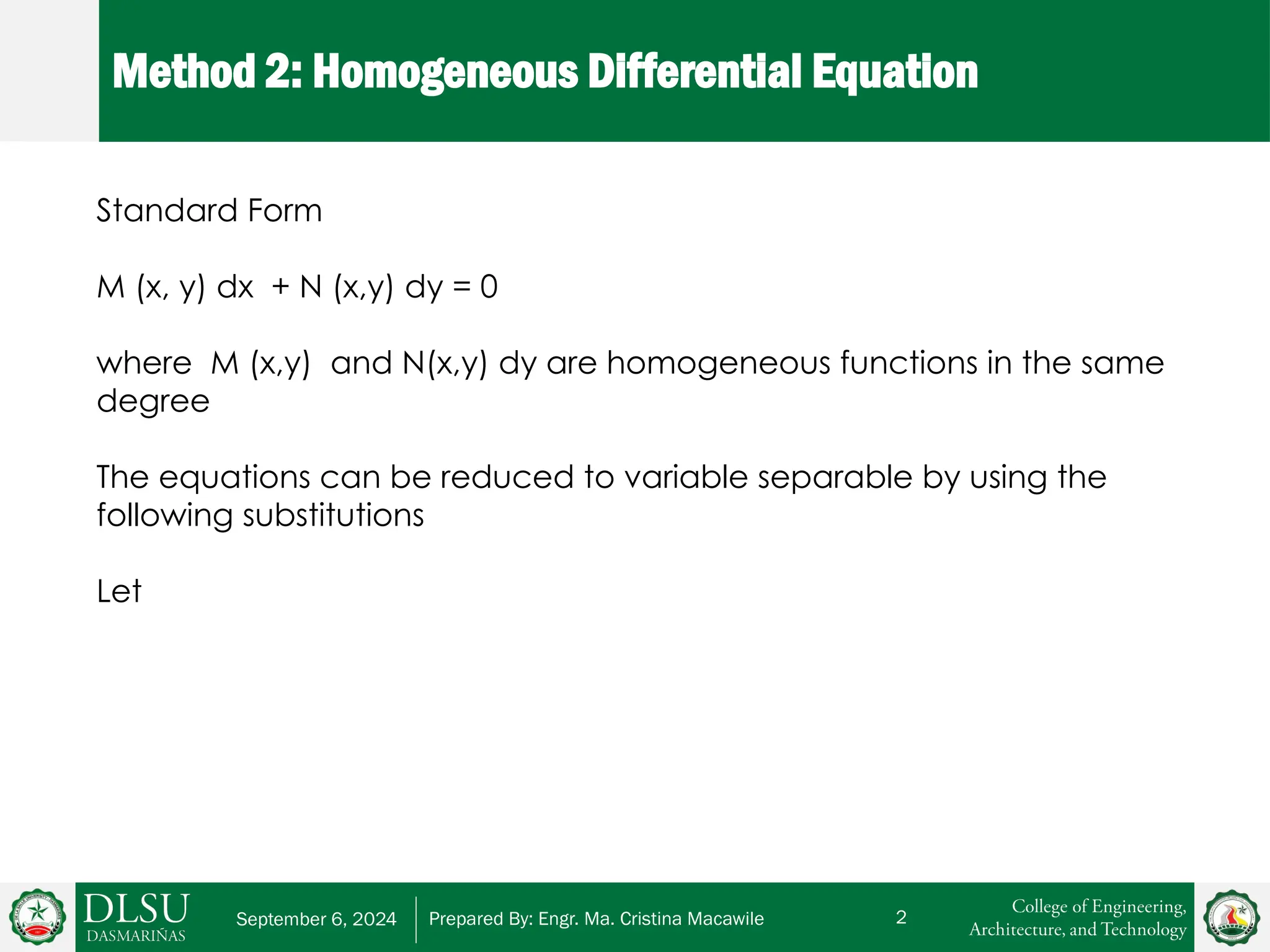
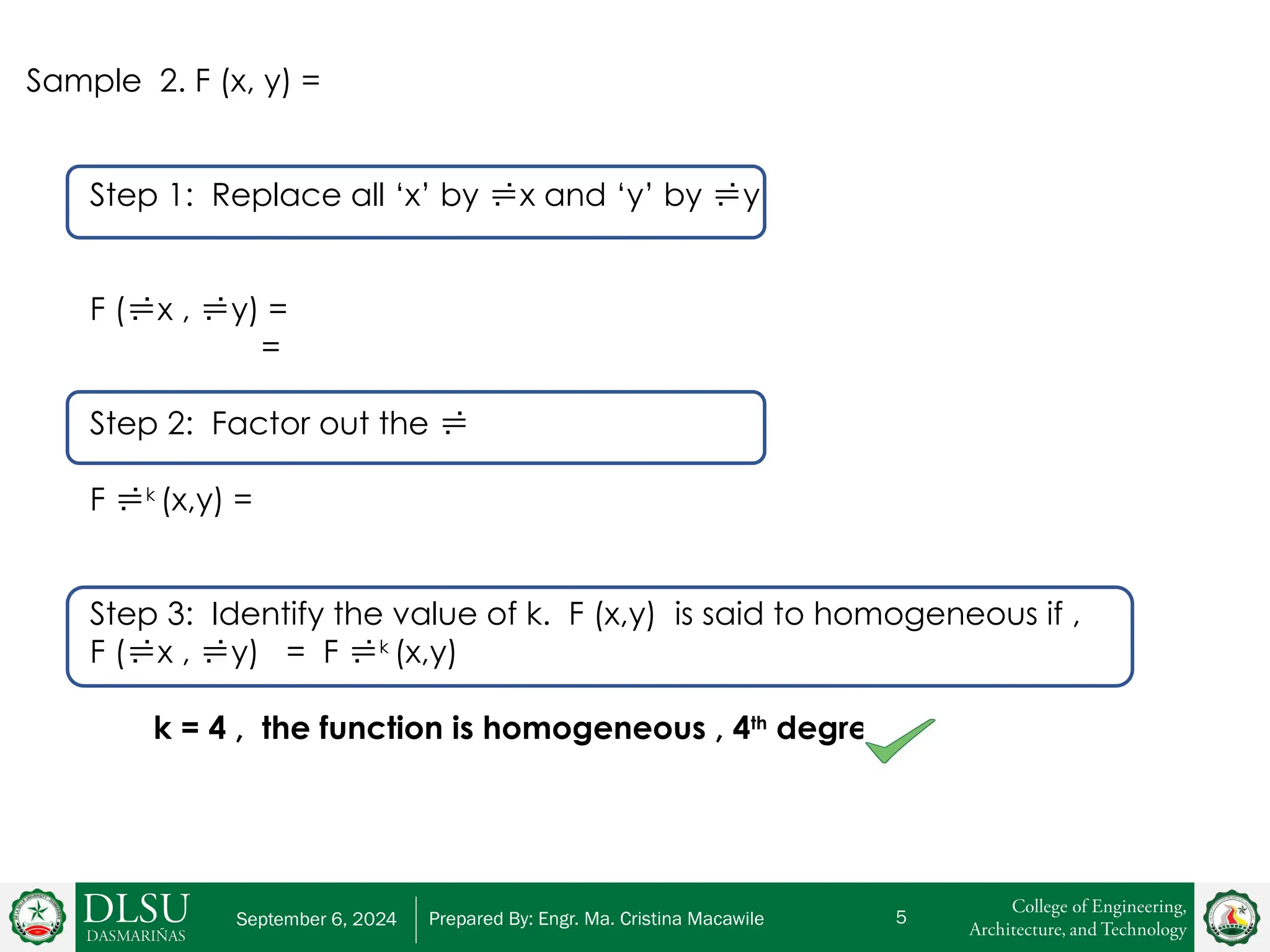
The document provides an explanation of homogeneous differential equations, detailing their standard form and characteristics. It includes methods for determining homogeneity and examples demonstrating the steps for solving both general and particular solutions. Key concepts covered include identifying the degree of homogeneity and applying the variable separable method.