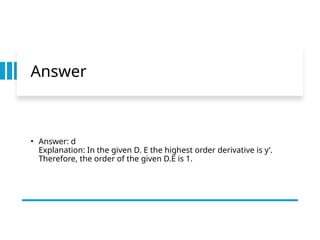
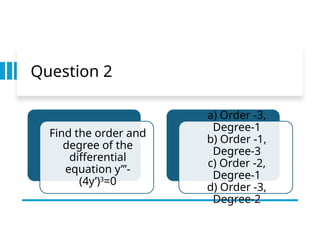
The document provides an overview of differential equations, covering definitions, classifications based on order and linearity, and solutions including general and particular forms. It explains concepts such as order, degree, homogeneous and linear differential equations, as well as the method to solve first-order linear differential equations. Additionally, it includes examples and questions to illustrate these concepts.