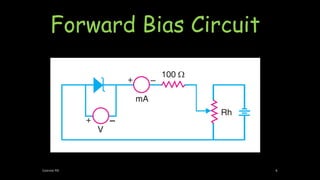
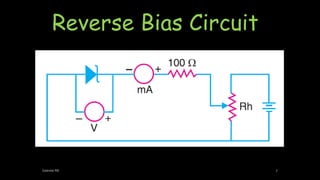
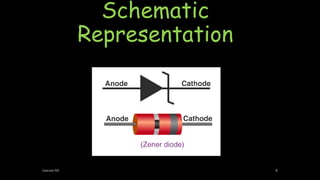
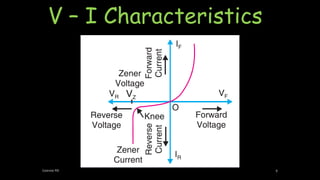
A Zener diode operates in the reverse breakdown region with a sharp breakdown voltage. It is an ordinary P-N junction diode that is properly doped to have a very sharp and almost vertical breakdown. It is designed to operate exclusively under reverse bias conditions in the breakdown region without damage. The breakdown voltage can range from 2V to 800V depending on the doping level. When reverse biased, a small reverse saturation current flows until the breakdown voltage is reached, at which point the reverse current increases sharply. This breakdown voltage is called the Zener voltage and remains constant even as the Zener current increases considerably, allowing the Zener diode to be used for voltage regulation.