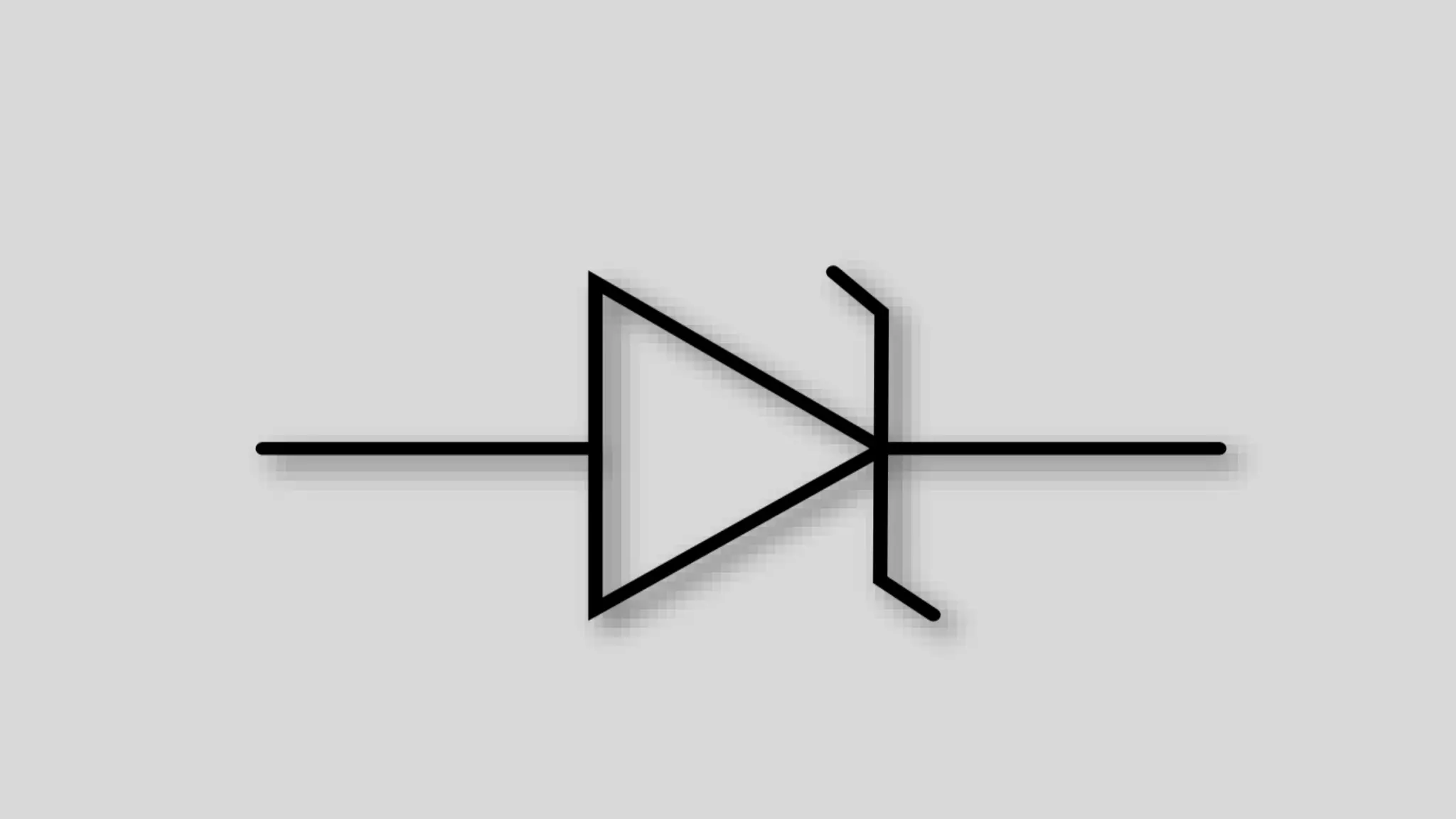
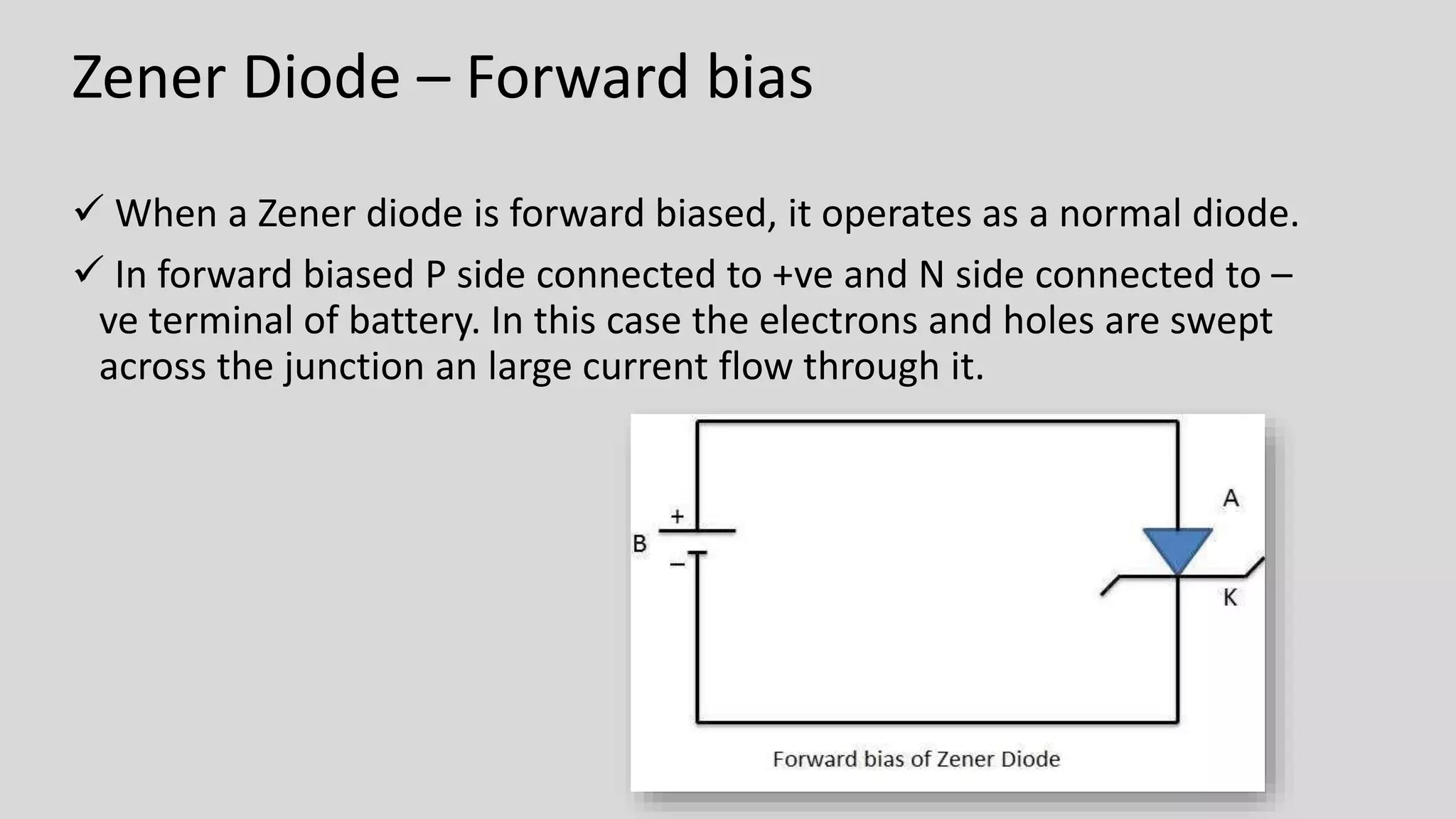
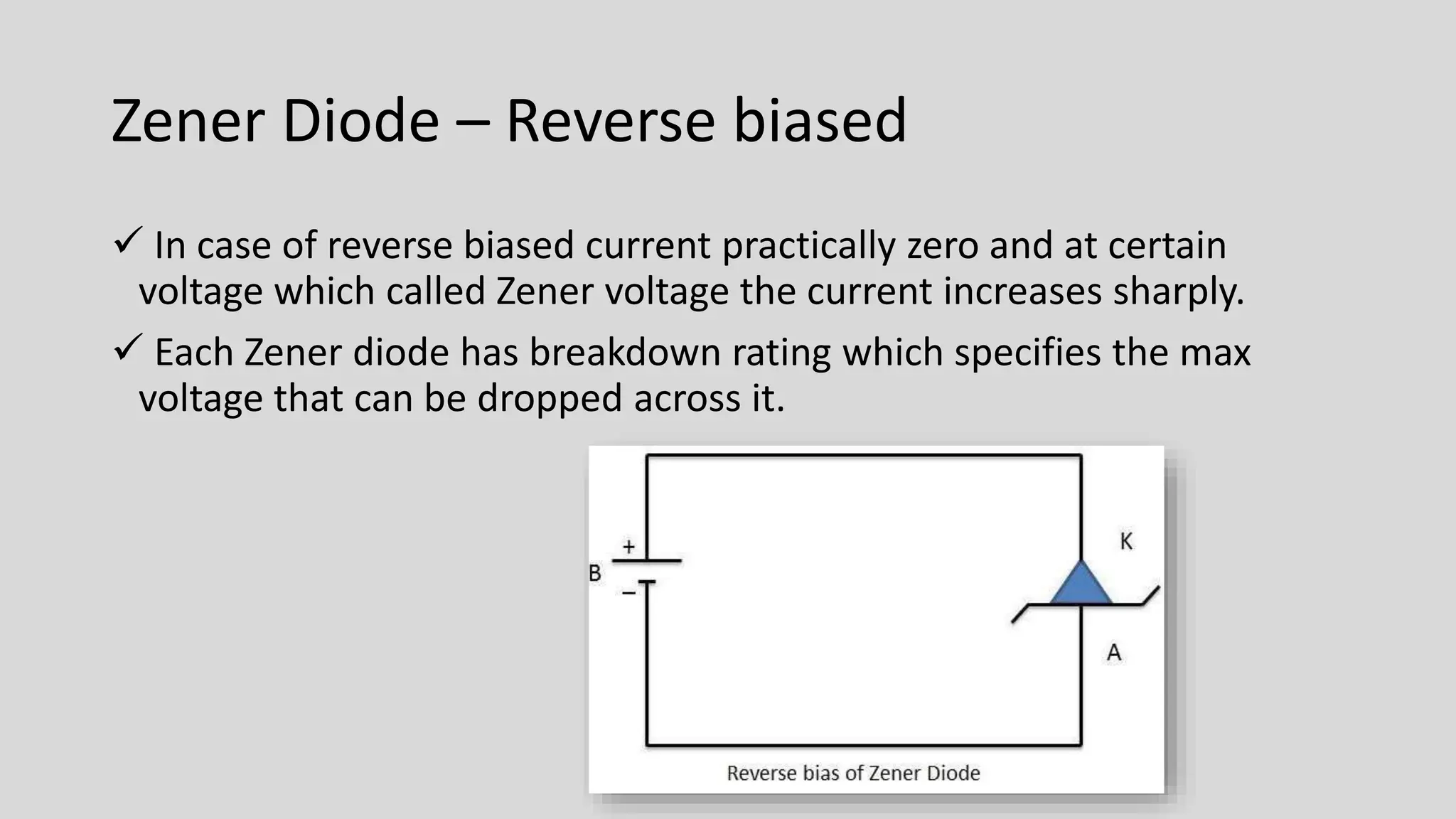
This document provides information about Zener diodes. It begins by listing the group members and then describes the key differences between regular diodes and Zener diodes. Zener diodes allow current to flow in both directions, unlike regular diodes, and can regulate voltage. The document discusses Clarence Zener, the physicist who discovered the property that Zener diodes exploit. It provides details on Zener diode symbols, how they operate under forward and reverse bias, their voltage regulation applications, and characteristics like breakdown voltage.