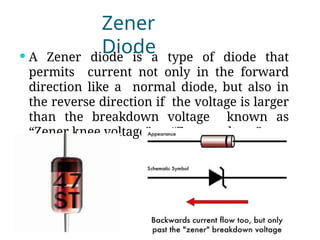
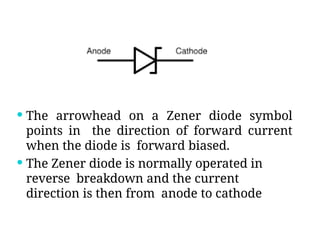
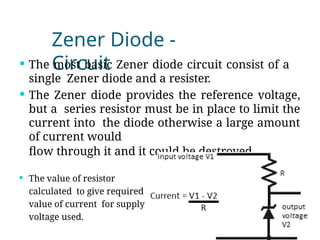
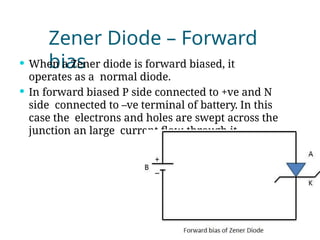
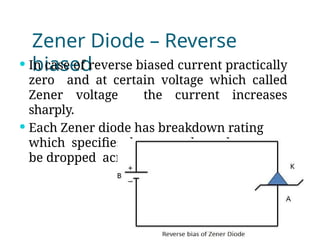
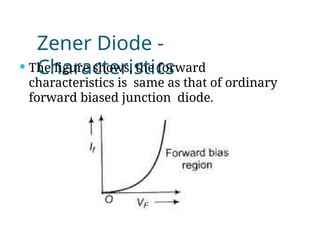
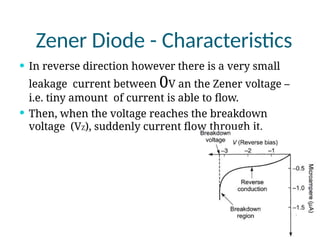
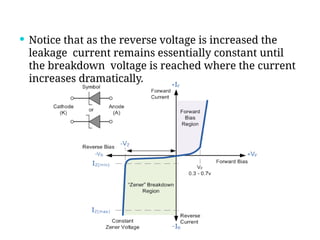
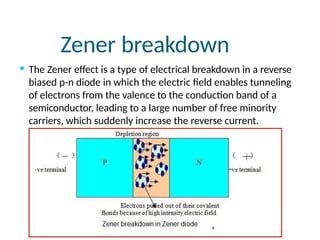
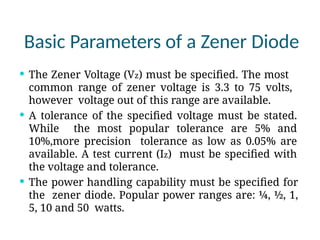
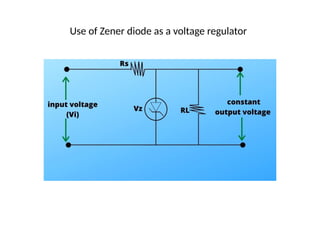
A diode is an electronic component with two electrodes (anode and cathode) that allows current to flow in one direction, while a zener diode can conduct in both forward and reverse directions at a specific breakdown voltage known as the zener voltage. Zener diodes are commonly used in circuits for voltage regulation and have characteristic behaviors in both forward and reverse bias states, including leakage current until breakdown is reached. Basic specifications for zener diodes include zener voltage, tolerance levels, and power handling capability, making them essential in various applications like zener regulators and power supplies.