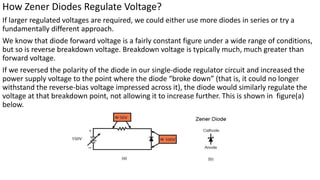
1. The report discusses the working of a Zener diode and how it can be used as a voltage regulator. It explains that a Zener diode allows current to flow in the reverse direction when the Zener voltage is reached.
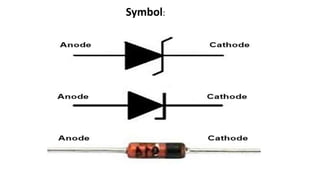
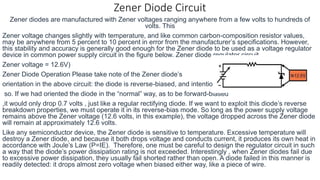
2. The report includes the symbol of a Zener diode and provides a circuit diagram showing how a Zener diode can regulate voltage. It explains that the voltage across a Zener diode remains constant over a range of currents.
3. Resources on Zener diodes and voltage regulators are cited at the end to provide additional information on the topic.