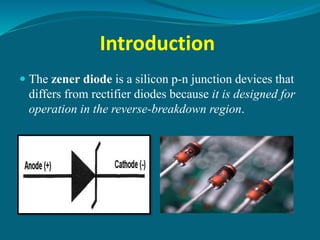
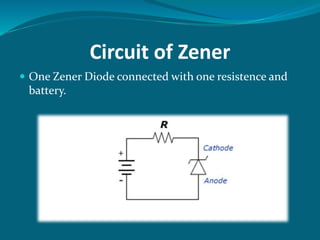
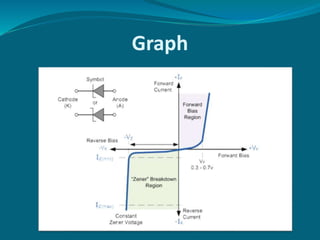
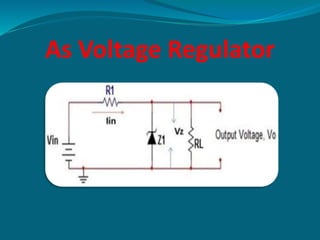
The document discusses the zener diode, emphasizing its design for operation in the reverse-breakdown region and its use as a voltage regulator. It explains two types of breakdown: zener breakdown, which occurs at lower reverse voltages, and avalanche breakdown, which occurs at higher reverse voltages. The zener diode maintains a constant voltage across it in a circuit, making it valuable for providing stable output voltage despite changes in current.