This document discusses extrusion, including its history, types of extruders, components of extruders, and applications. It covers key topics like:
- Extrusion gained popularity due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and high productivity.
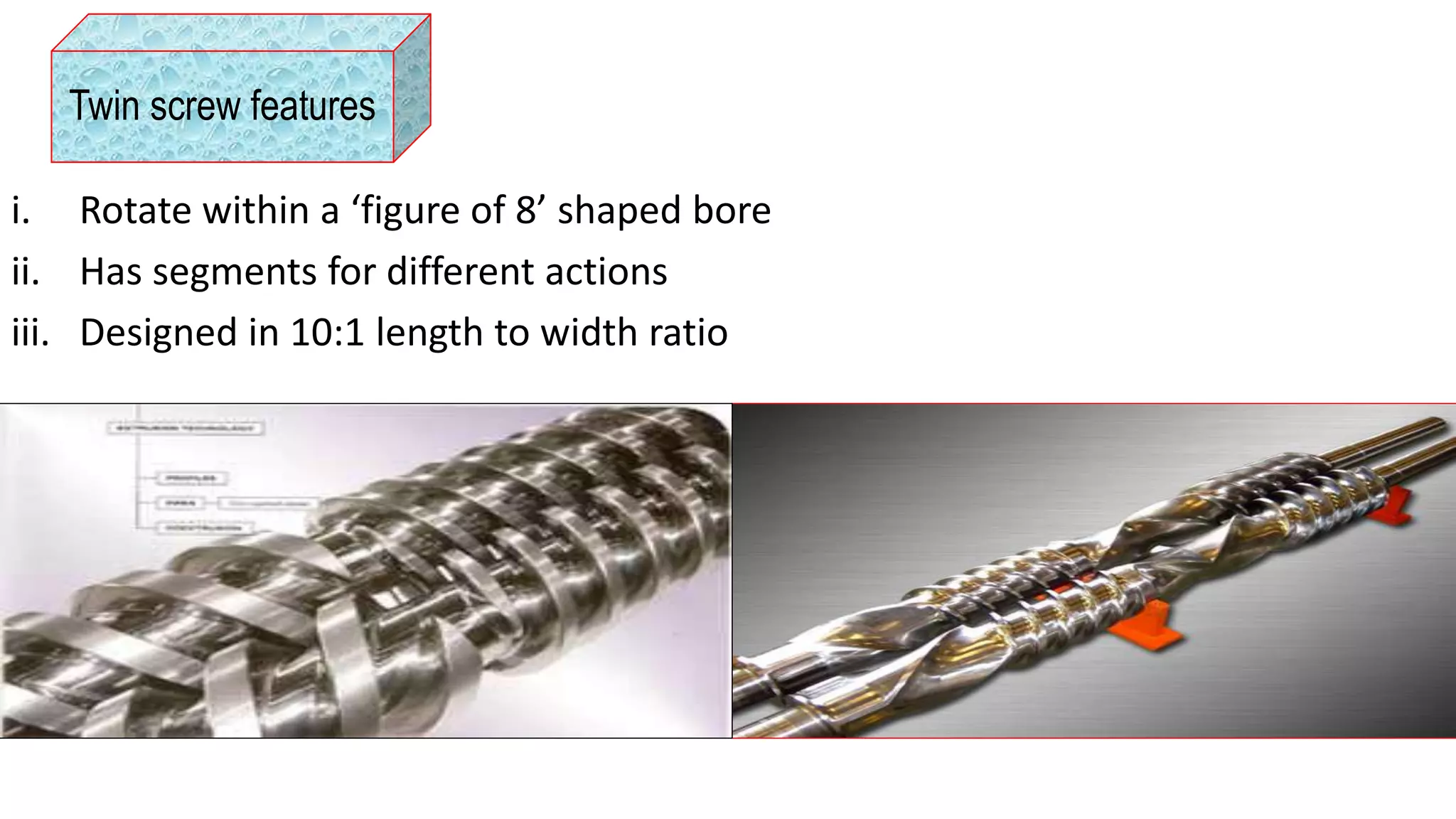
- The main types of extruders are single-screw and twin-screw extruders. Twin-screw extruders can be co-rotating or counter-rotating.
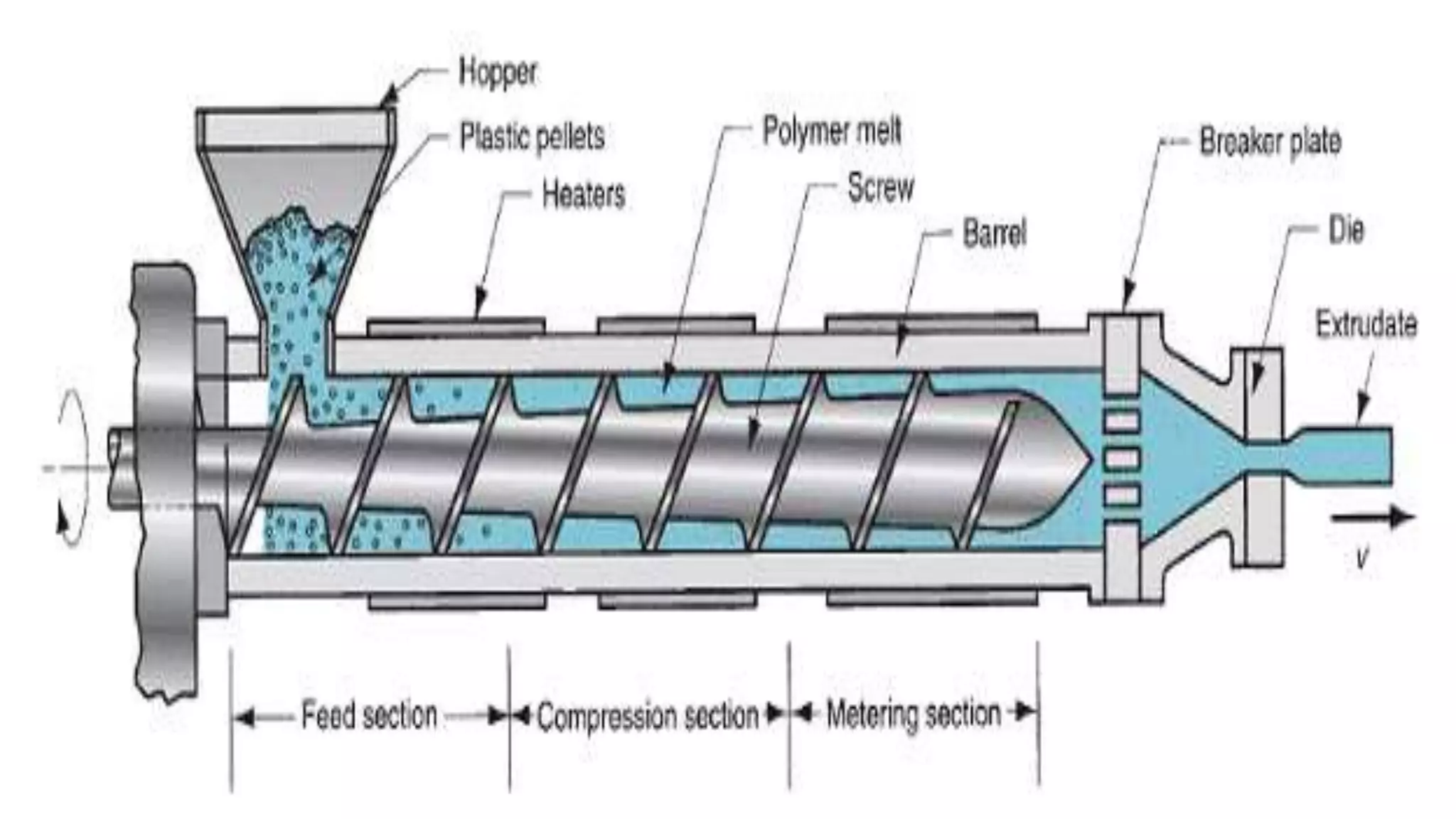
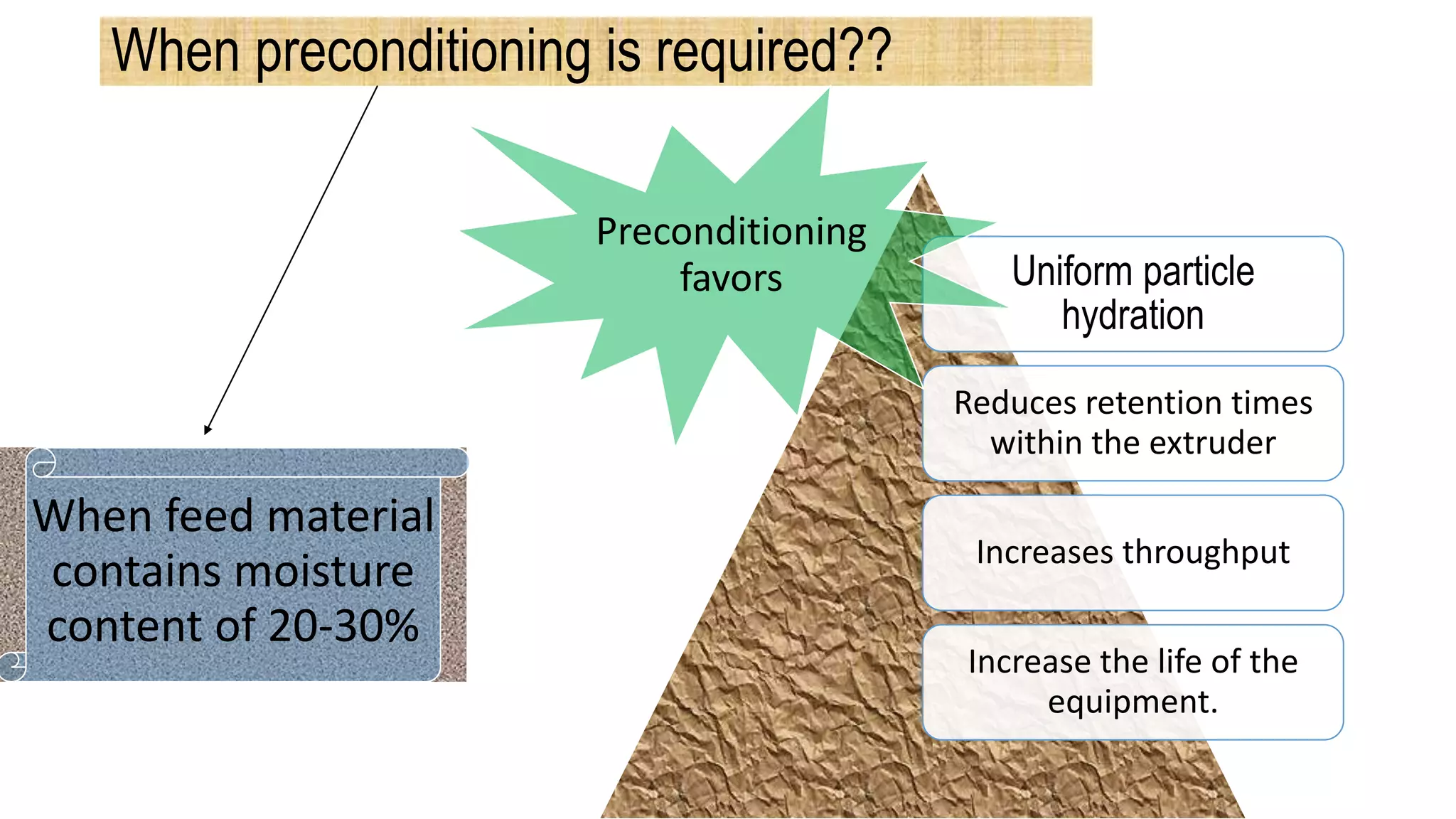
- Extruders consist of major components like the pre-conditioning system, feeding system, screw, barrel, and die.
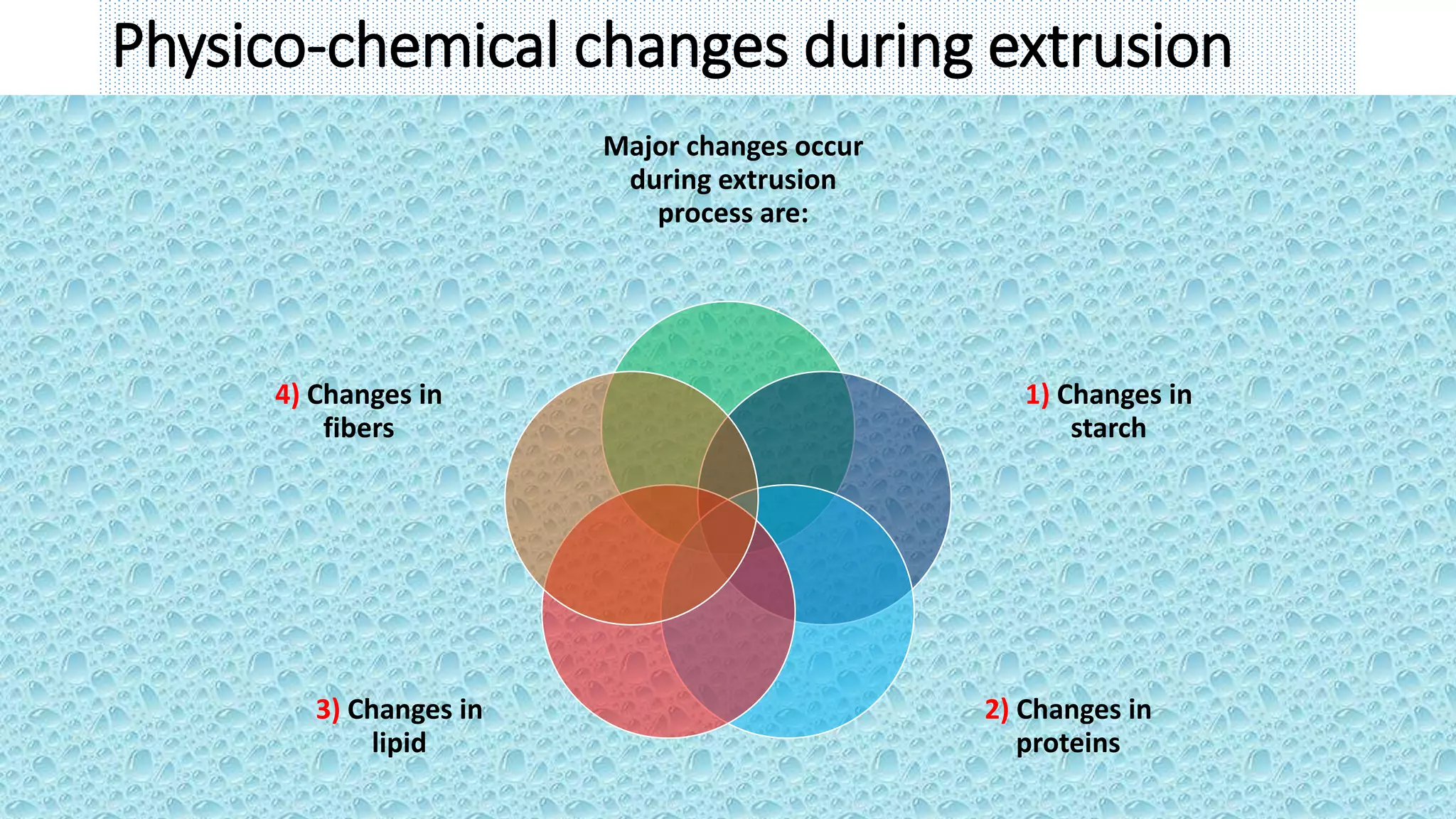
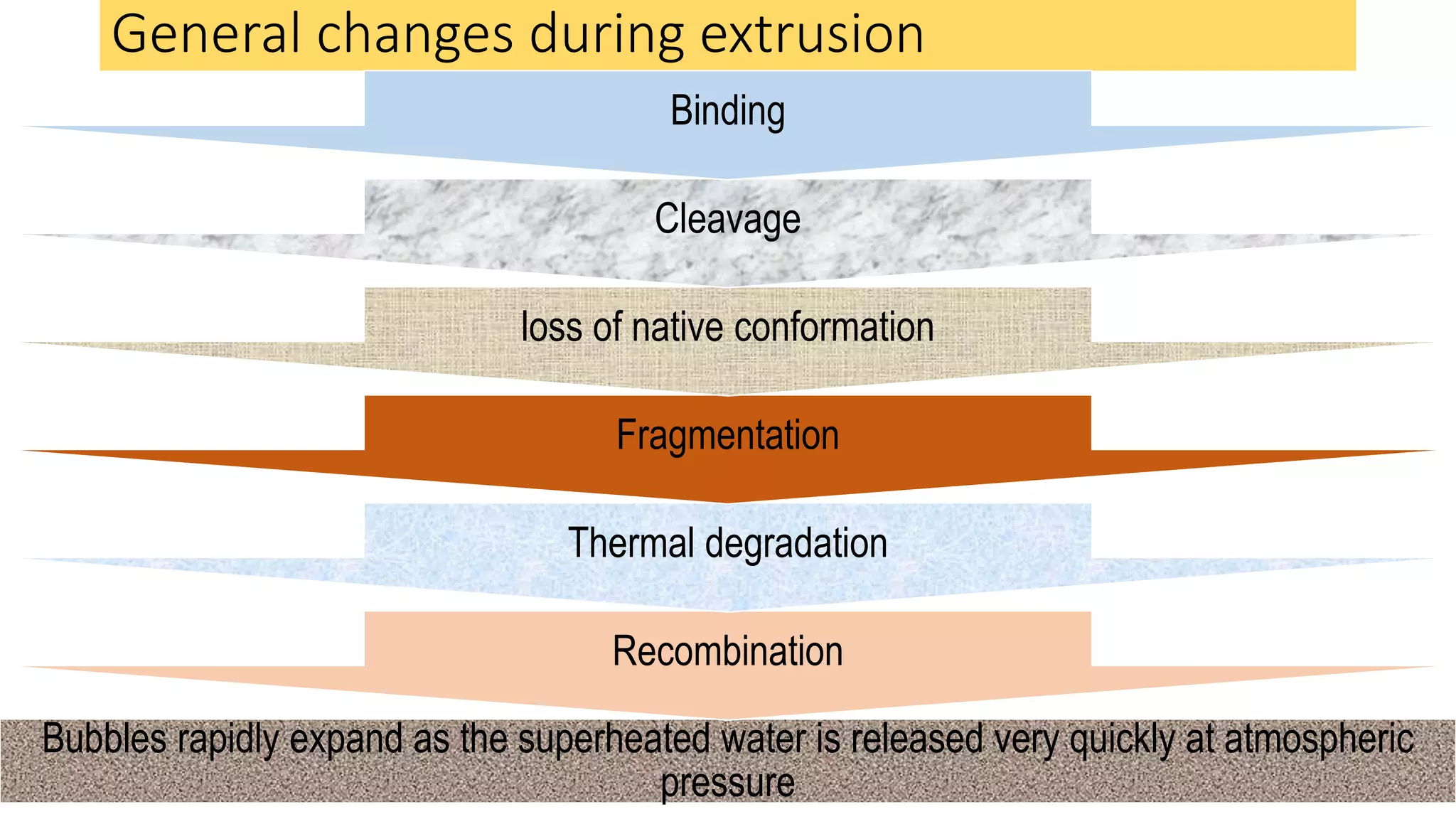
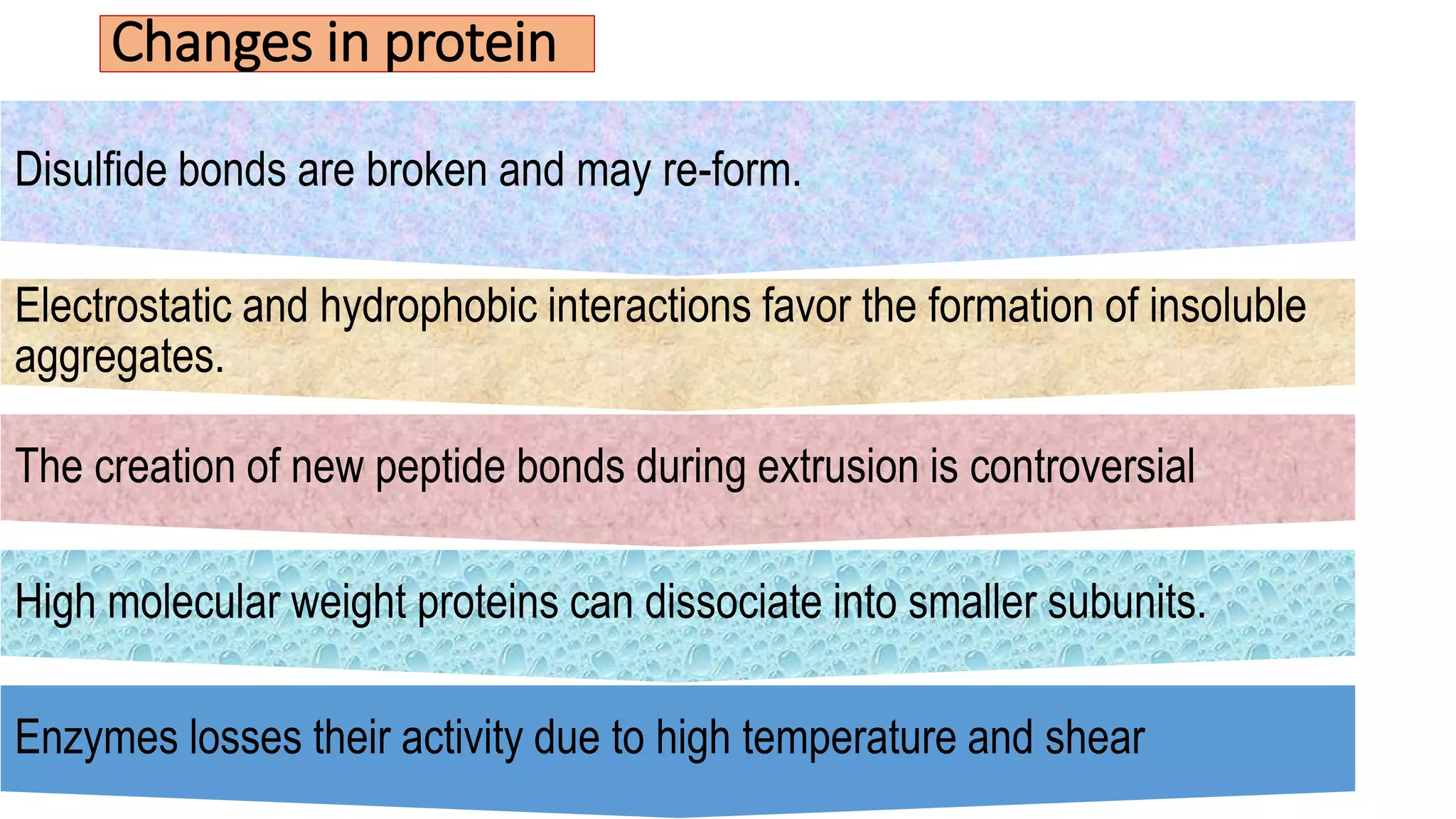
- During extrusion, physicochemical changes occur like starch gelatinization, protein denaturation, and