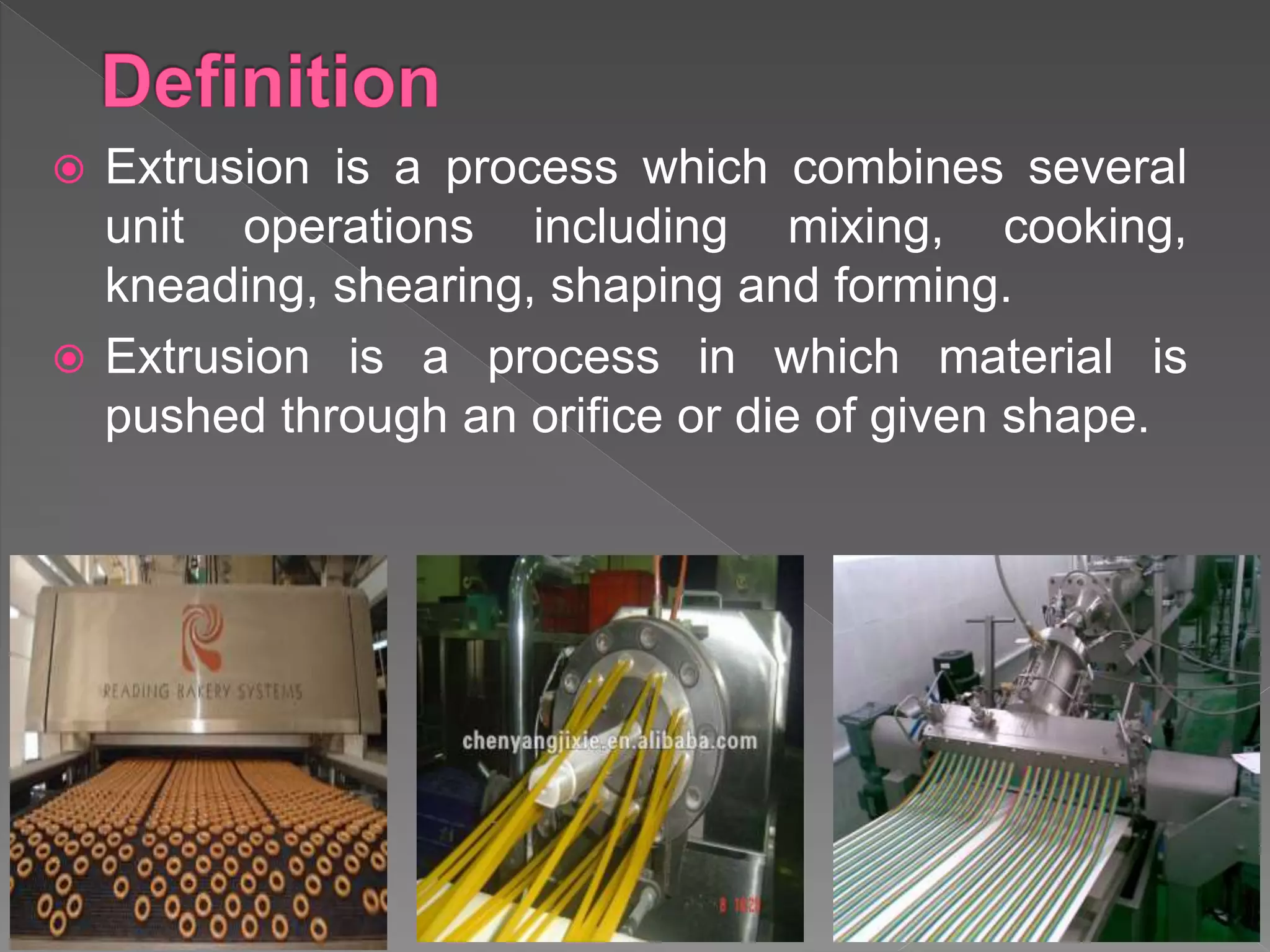
The document discusses the process of extrusion. It begins by defining extrusion as a process that combines mixing, cooking, kneading, shearing, shaping and forming. It then explains that extrusion involves pushing material through a die of a given shape. The key steps of extrusion including feeding, mixing, conveying material through a barrel, compressing it, and forcing it through a die are outlined. The document also categorizes and discusses different types of extruders and their applications in food processing.