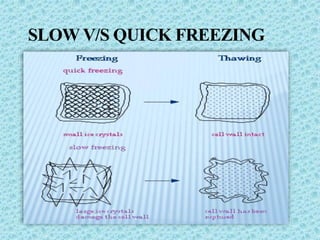
The document discusses the process of Individual Quick Freezing (IQF) for herbs, emphasizing its advantages in preserving taste, texture, and nutritional value while minimizing microbial growth. It details the steps involved in raw material preparation, washing, slicing, freezing, and quality checks, as well as the specifications for various herbs like chives, dill, and lemon grass. Key aspects include the freezing process, equipment used, and the importance of maintaining hygiene and safety standards throughout the operation.