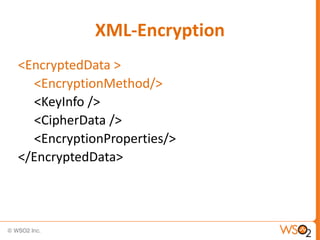
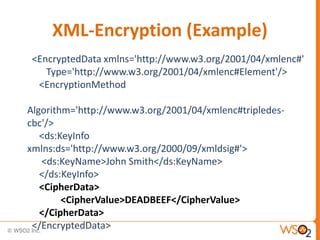
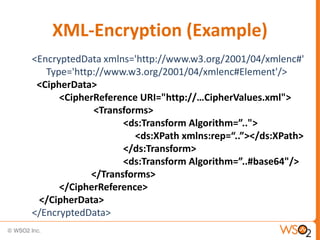
The document discusses XML Encryption, which is a W3C standard for encrypting XML documents and data. It can encrypt entire documents, parts of documents, or external objects. XML Encryption uses symmetric or asymmetric encryption and supports algorithms like AES and Triple DES. It provides elements for specifying the encryption method, key information, and encrypted data or references to encrypted resources. The key information does not directly include the encryption key but provides ways to locate it through names, encryption, or key agreement protocols.


























![XML-Encryption - Processing
• Choose an encryption algorithm
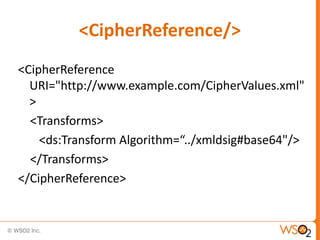
<EncryptionMethod/>
• Obtain an encryption key and may represent it
• Serialize message data to octets [ a stream of
bytes]
• Encrypt the data
• Specify the <EncryptedData Type=“”>
• Complete the <EncryptedData> structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xml-encryption-131128012554-phpapp01/85/XML-Encryption-34-320.jpg)