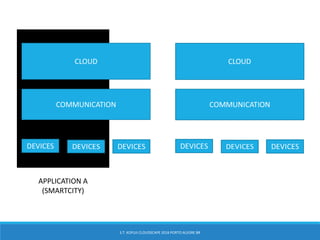
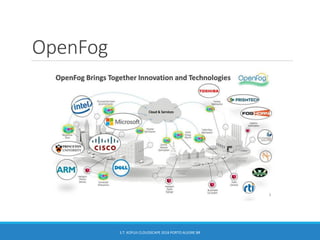
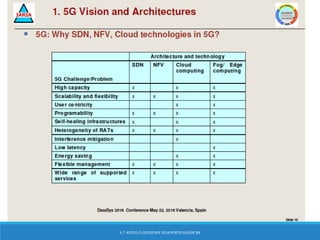
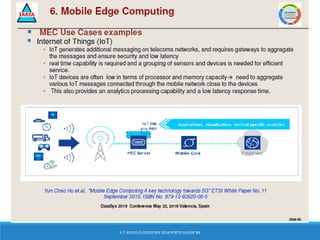
The document discusses the integration of 5G, cloud, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, highlighting their importance for digital market standardization. It addresses the challenges of mobile edge computing and the need for efficient cloud-based solutions that cater to various industries while managing security and operational challenges. Furthermore, it emphasizes the role of collaboration between industry and academia in innovating solutions to ensure interoperability and address barriers related to infrastructure and standards.