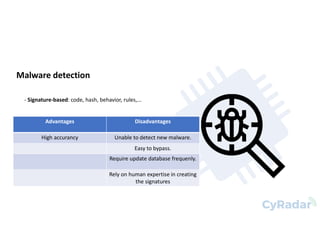
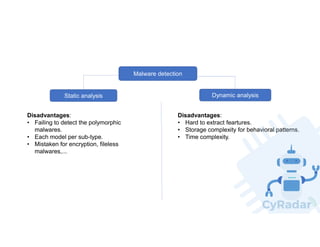
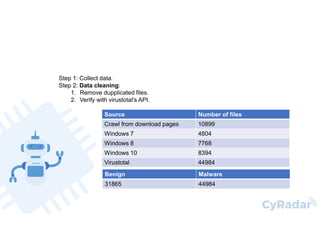
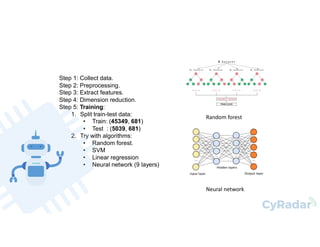
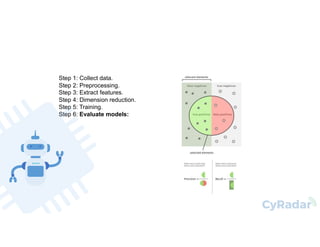
This document discusses using machine learning and deep learning for malware detection. It notes that over 350,000 new malware are created daily, posing a significant threat. Traditional signature-based detection has limitations in detecting new malware. The document reviews research applying machine learning and deep learning techniques to malware detection using static and dynamic analysis of features. It then describes the authors' approach of using opcode frequency models with random forest and neural networks to classify files, achieving 97-98% precision and recall on a test set. The conclusion is that machine learning and deep learning can help address limitations of traditional approaches by enabling detection of new malware.