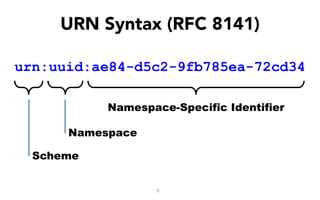
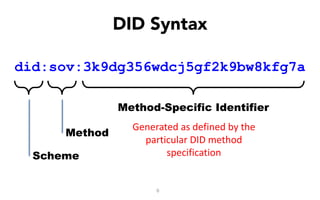
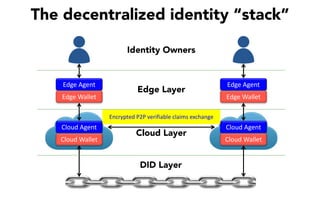
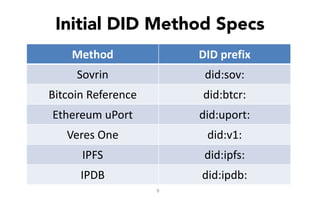
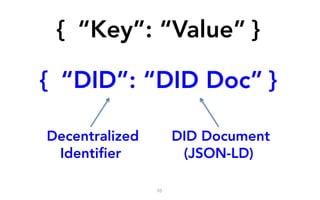
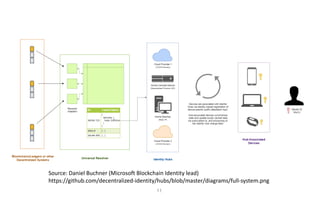
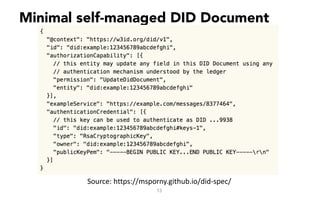
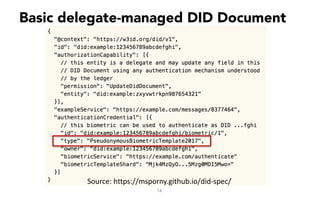
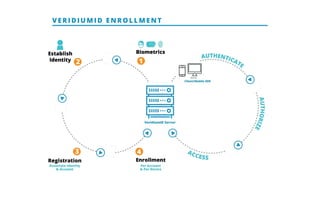
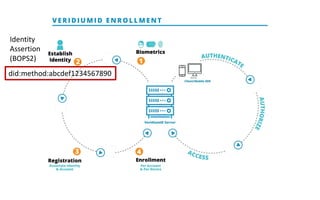
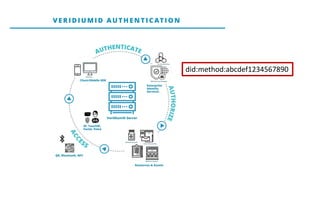
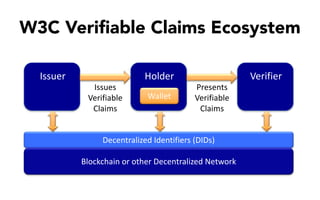
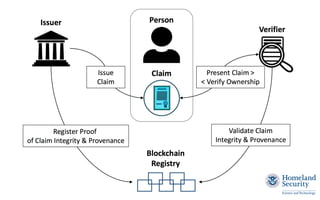
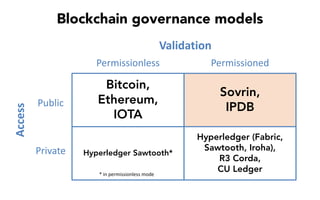
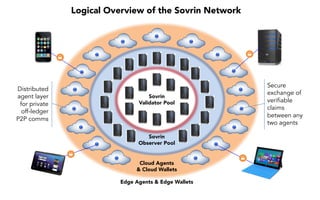
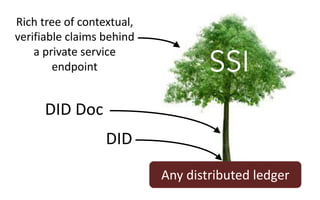
This document discusses self-sovereign identity and decentralized identifiers (DIDs). It provides an overview of identity evolution from centralized to user-centric models. Self-sovereign identity allows individuals to control their digital identities across systems without relying on centralized authorities. DIDs are a new type of identifier that can be registered on a distributed ledger without a centralized registration authority. The document outlines the goals and components of DID specifications and describes how DIDs and verifiable claims work on networks like Sovrin to enable self-sovereign identity.