Embed presentation
Download to read offline

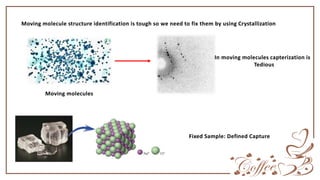
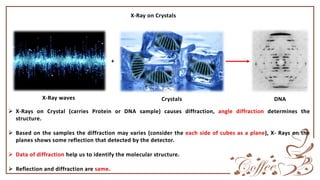
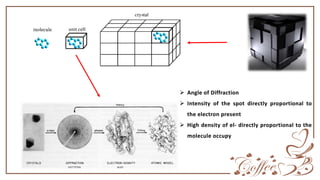

X-ray crystallography is used to determine the structure of molecules like proteins and DNA by fixing samples into crystals and bombarding them with X-rays. The X-rays cause diffraction patterns based on the molecular structure, with different angles of diffraction indicating different planes of the crystal structure. Analysis of the diffraction data reveals information about electron density and molecular structure that allows researchers to identify the positions of atoms within the sample.




