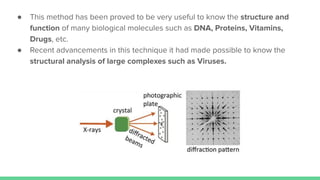
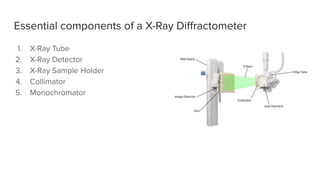
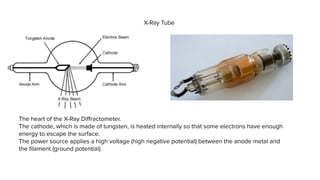
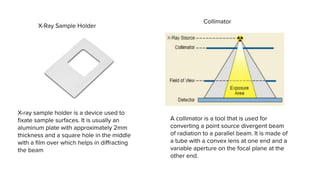
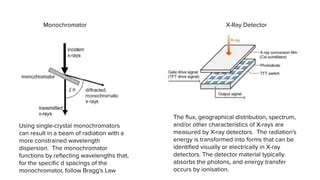
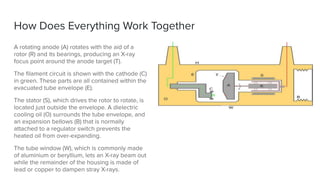
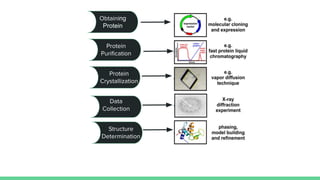
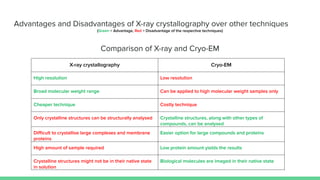
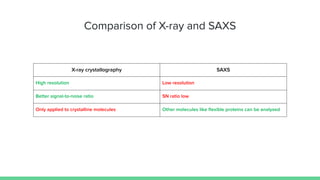
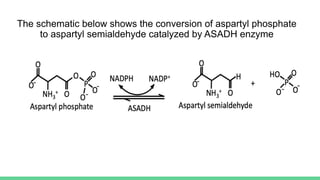
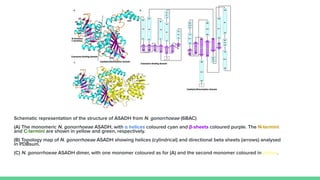
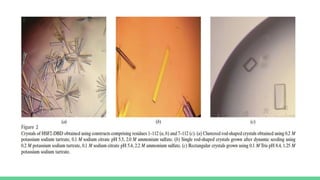
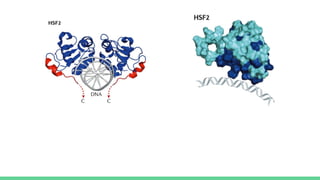
X-ray crystallography is a technique for determining the atomic structure of crystals using X-ray diffraction, which allows for the mapping of electron density and spatial distribution of atoms in a crystal. Important historical contributions were made by scientists such as Röntgen, Bragg, and Hodgkin, with various Nobel prizes awarded for advancements in the field. The technique has applications in biology and chemistry, such as in understanding the structures of essential enzymes and biological molecules, while offering advantages and disadvantages compared to other methods like cryo-EM and NMR.