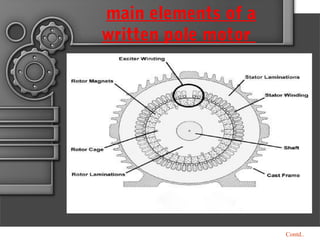
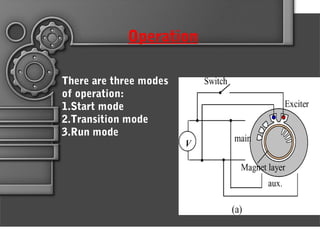
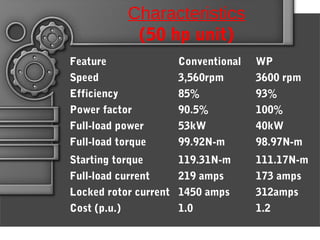
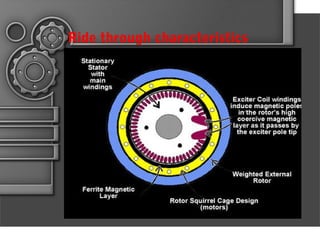
Written-pole electric motors utilize concepts from induction, hysteresis, and permanent magnet motors. They allow speed and frequency to be independent by enabling a controlled variable number of poles through a "writing" coil. This overcomes limitations of conventional motors having a fixed number of poles. A written-pole motor consists of a rotor layer and excitation winding to magnetize portions of the rotor. It operates in start, transition, and run modes. Compared to conventional motors, written-pole motors have lower starting current, higher efficiency, unity power factor, and can ride through power disturbances. Their main applications are for irrigation pumps and systems where three-phase power is unavailable.