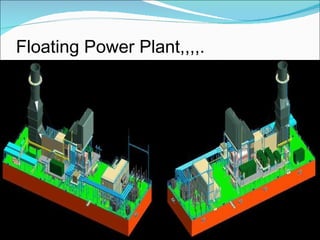
Floating power plants (FPPs) are mobile offshore power generation facilities that can be rapidly deployed to supply electricity to areas in need. One of the earliest FPPs was constructed in 1940 in the Philippines and is still operational today in Ecuador. Countries in Southeast Asia and South America have utilized FPPs to address severe power shortages. FPPs are designed to operate like ships on water, generating power while remaining stable without rotational movement as water levels change. Recent FPP developments include diesel, wind, and tidal energy powered models.