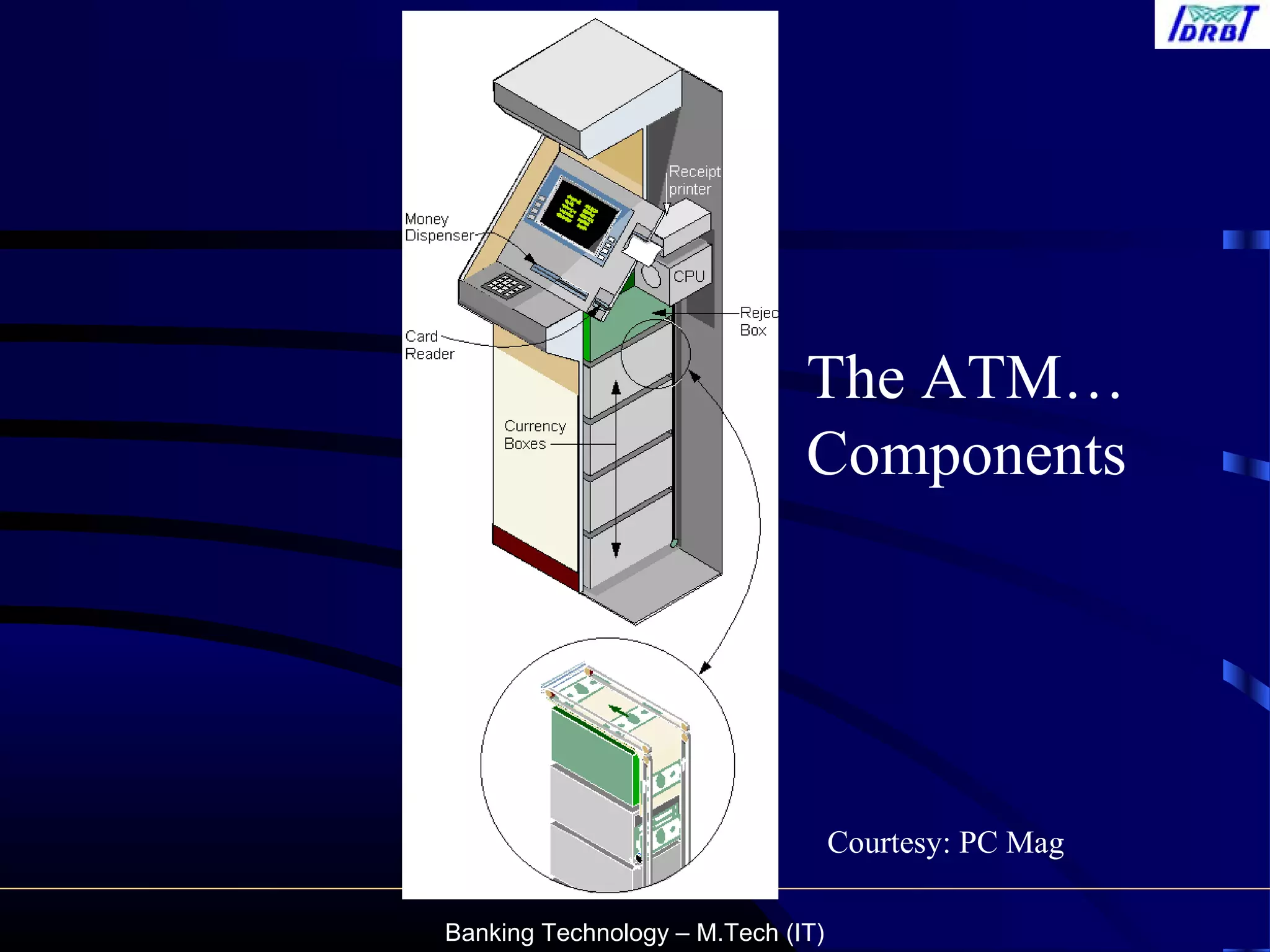
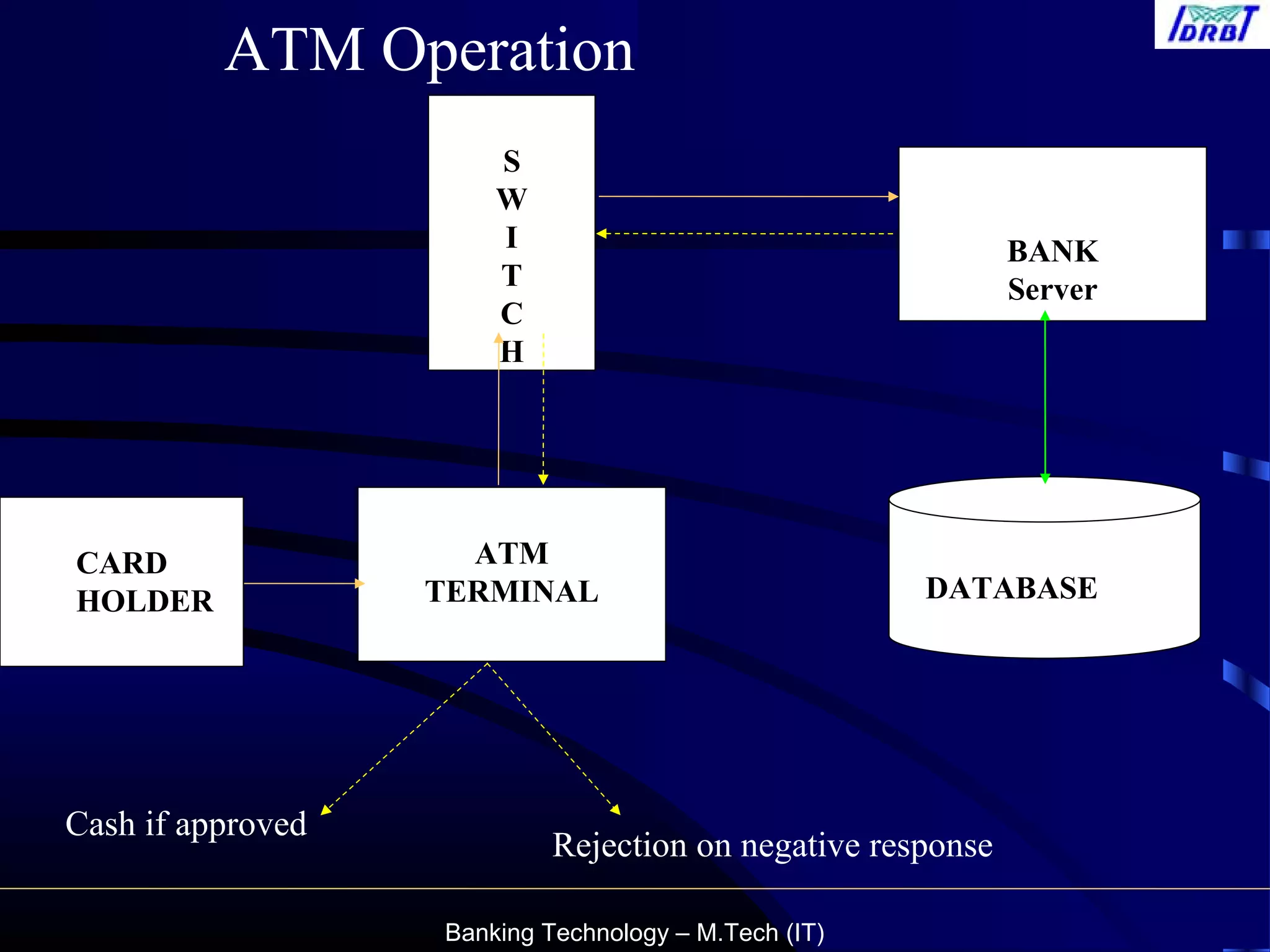
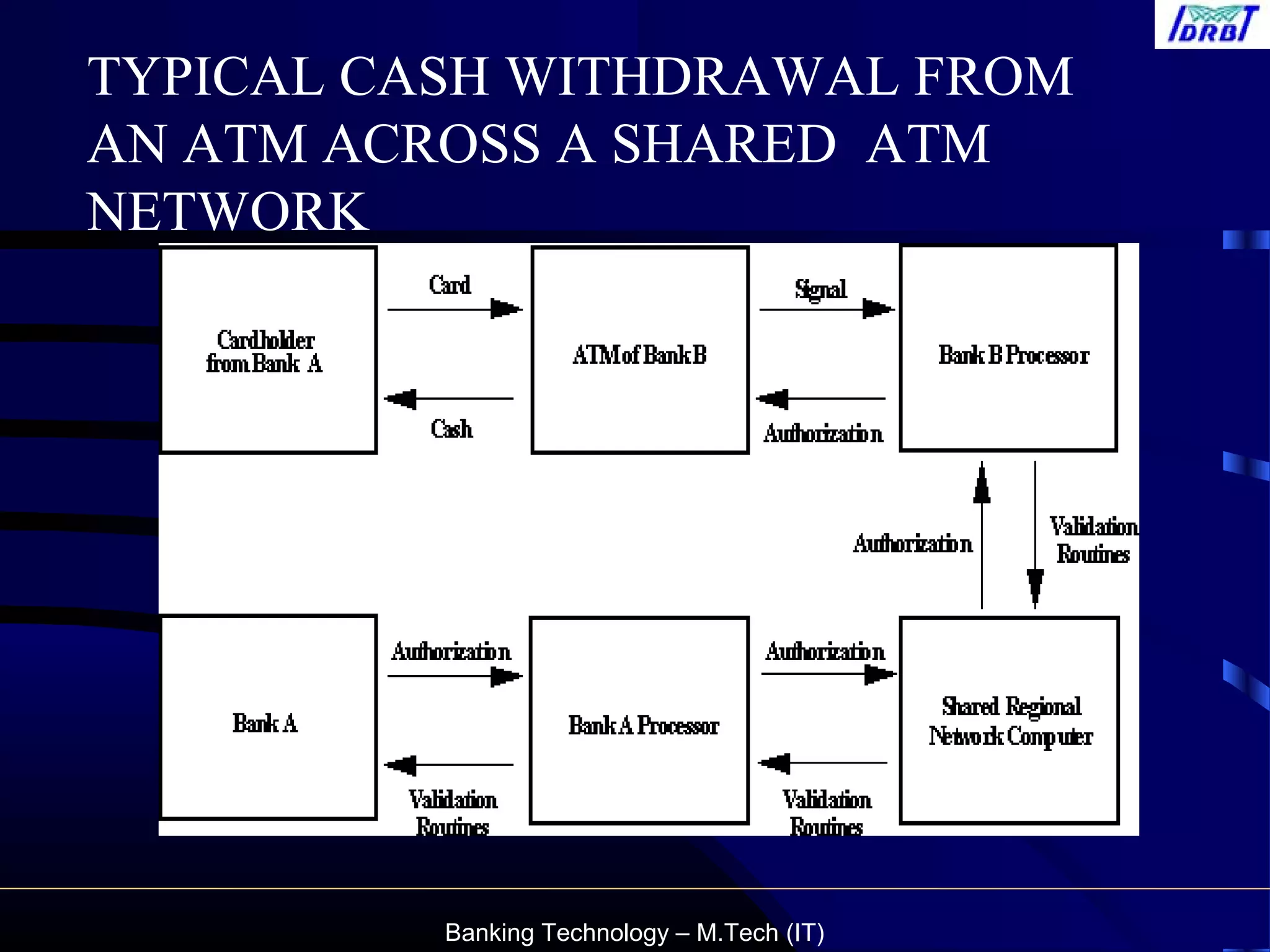
This document provides an overview of automated teller machine (ATM) technology and operations. It discusses the types and components of ATMs, how ATM transactions work across shared networks, security features to prevent fraud, and the role of debit cards. It also summarizes the reconciliation process for ATM transactions and common fraud risks. The document aims to educate customers on safely using ATMs.