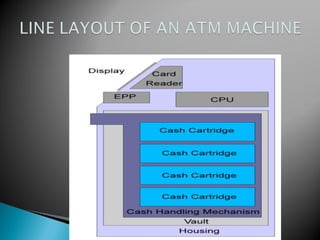
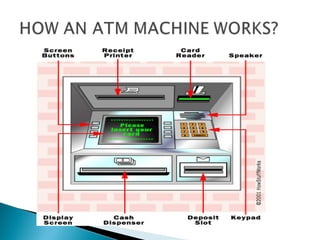
Technological developments in the banking sector include e-banking, core banking, mobile banking, and automated teller machines (ATMs). E-banking allows customers to bank electronically using internet and mobile devices. Core banking integrates banking services across branches on a single platform. Mobile banking provides banking services via mobile phones while ATMs allow customers to access basic banking services without human assistance. These technologies have improved customer convenience but also introduce some risks regarding system failures and cybercrime.