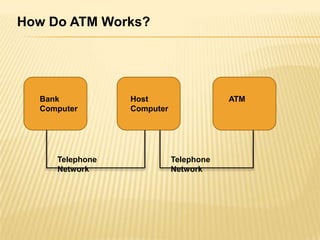
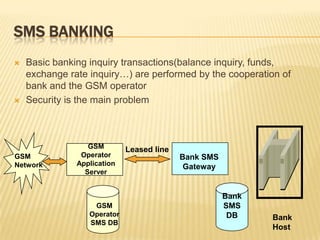
E-banking allows customers to perform banking transactions online through the bank's website or a mobile app. There are two main types of ATMs - leased-line ATMs that have a dedicated phone line and dial-up ATMs that use a normal phone line. ATMs have input devices like a card reader and keypad, and output devices like a display screen, receipt printer, and cash dispenser. Mobile banking applications include SMS banking, WAP banking, and STK banking. Security measures for e-banking include encryption, public/private key infrastructure, and keeping PIN numbers secret.