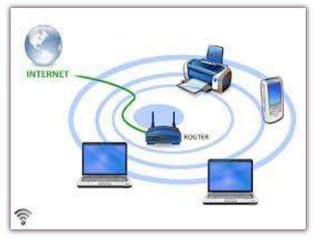
This document provides an overview of WiFi/IEEE 802.11 networking. It discusses the history and standards of WiFi, including 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. The working principle of WiFi and how devices connect to access points is described. Different WiFi network topologies are presented, along with the advantages of wireless connectivity and applications of WiFi technology.