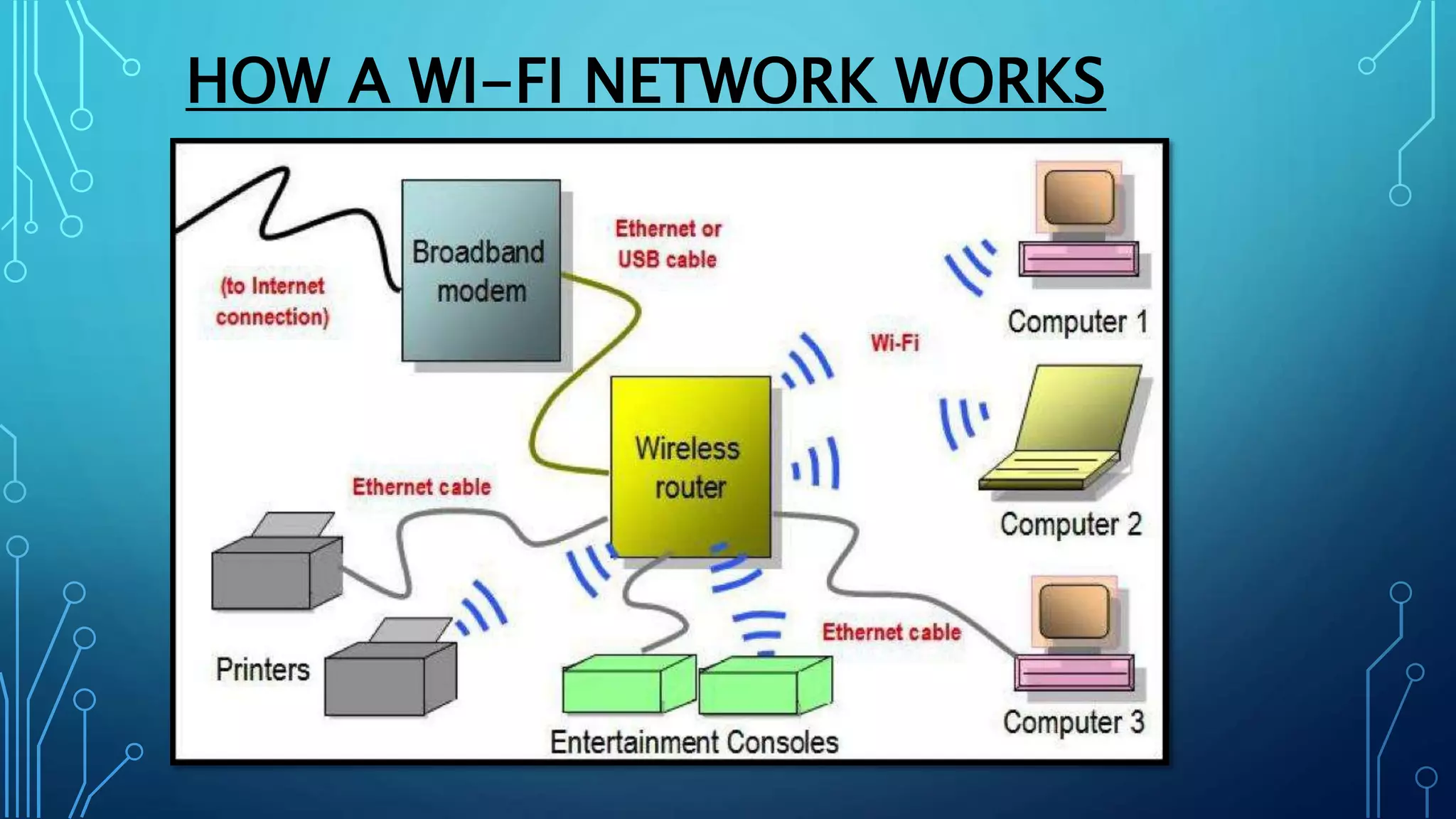
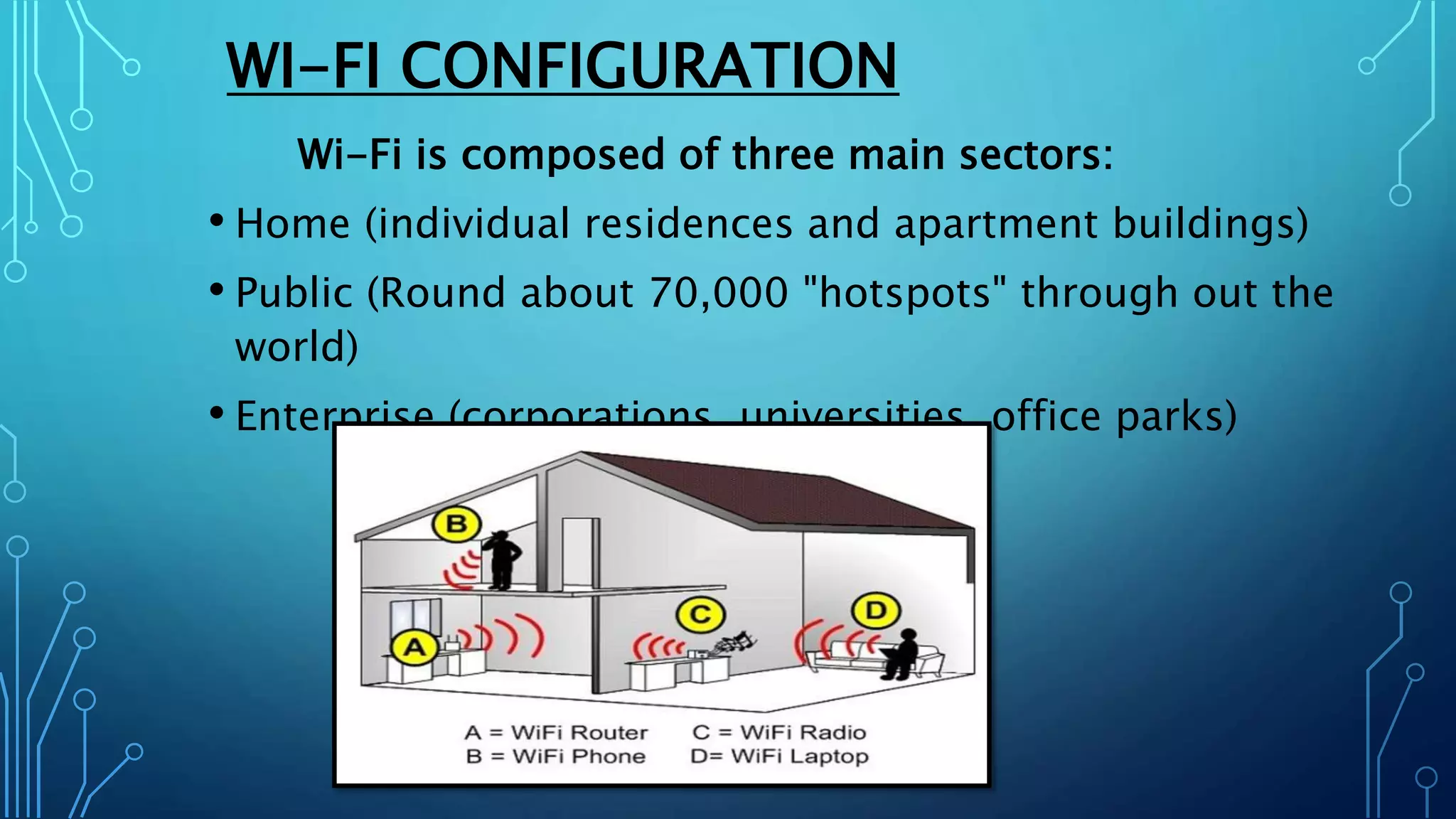
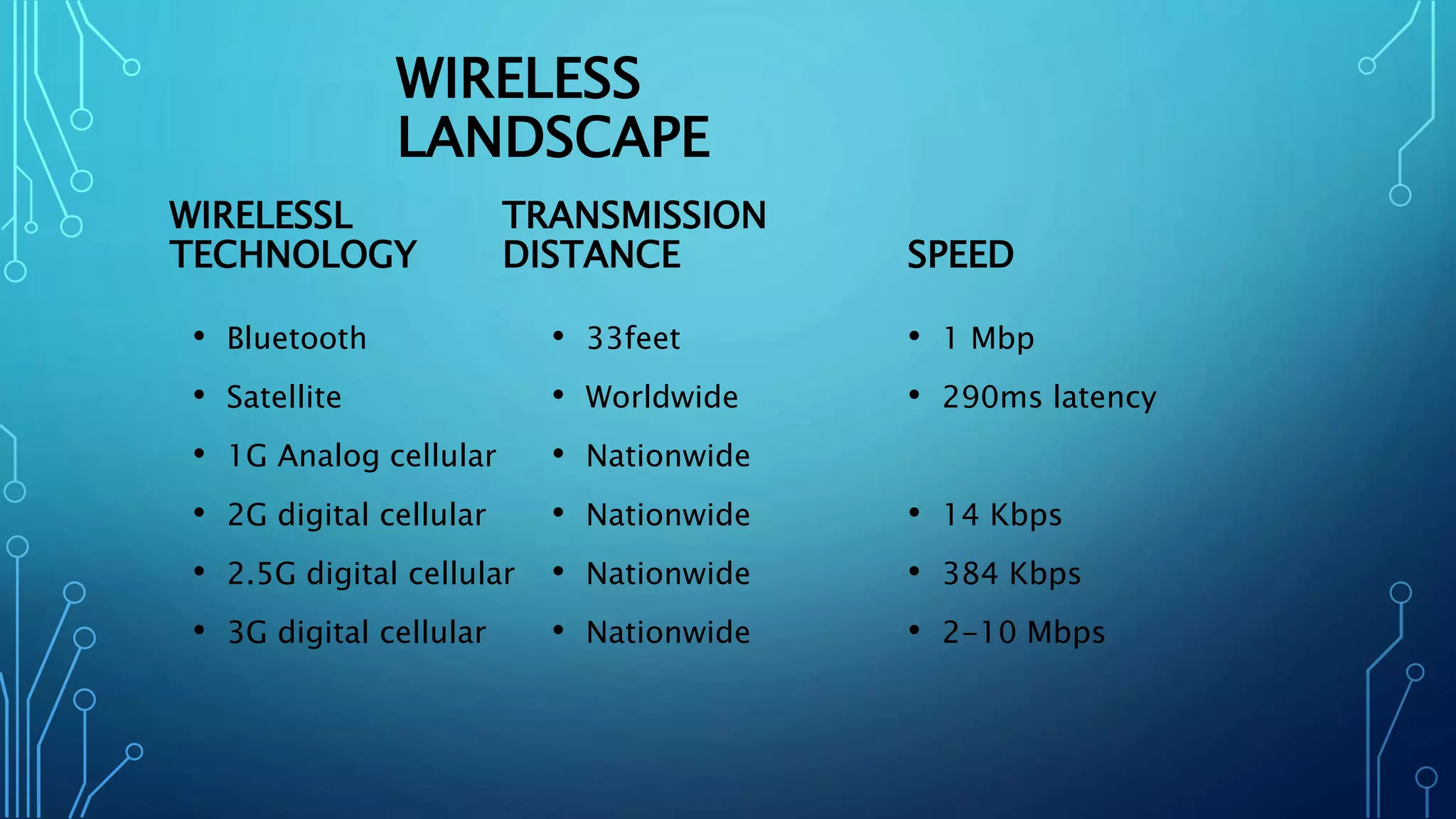
This document discusses Wi-Fi technology. It provides an introduction to Wi-Fi, describing how Wi-Fi networks work and the components involved like access points and Wi-Fi cards. It then covers the different Wi-Fi standards (802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g), how they operate and their benefits. The document also discusses Wi-Fi configuration, security methods to protect networks, and the advantages and limitations of Wi-Fi technology.