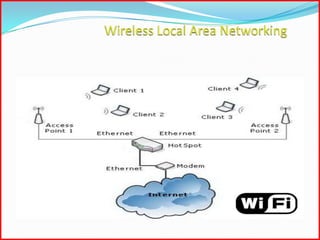
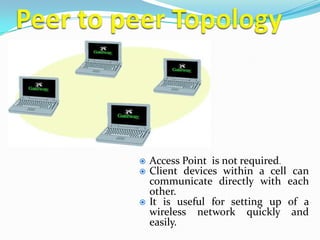
This document provides an overview of Wi-Fi technology, including its introduction, scope, working principles, and how to build a Wi-Fi network. Wi-Fi allows for wireless internet and network connectivity within a specific geographic area using radio waves. Common components of a Wi-Fi network include access points that act as base stations to connect wireless devices to the internet or a larger network within a range of 100-150 feet indoors. The document also discusses Wi-Fi security standards like WEP and WPA that aim to protect wireless networks, and examples of Wi-Fi usage in public places and businesses.