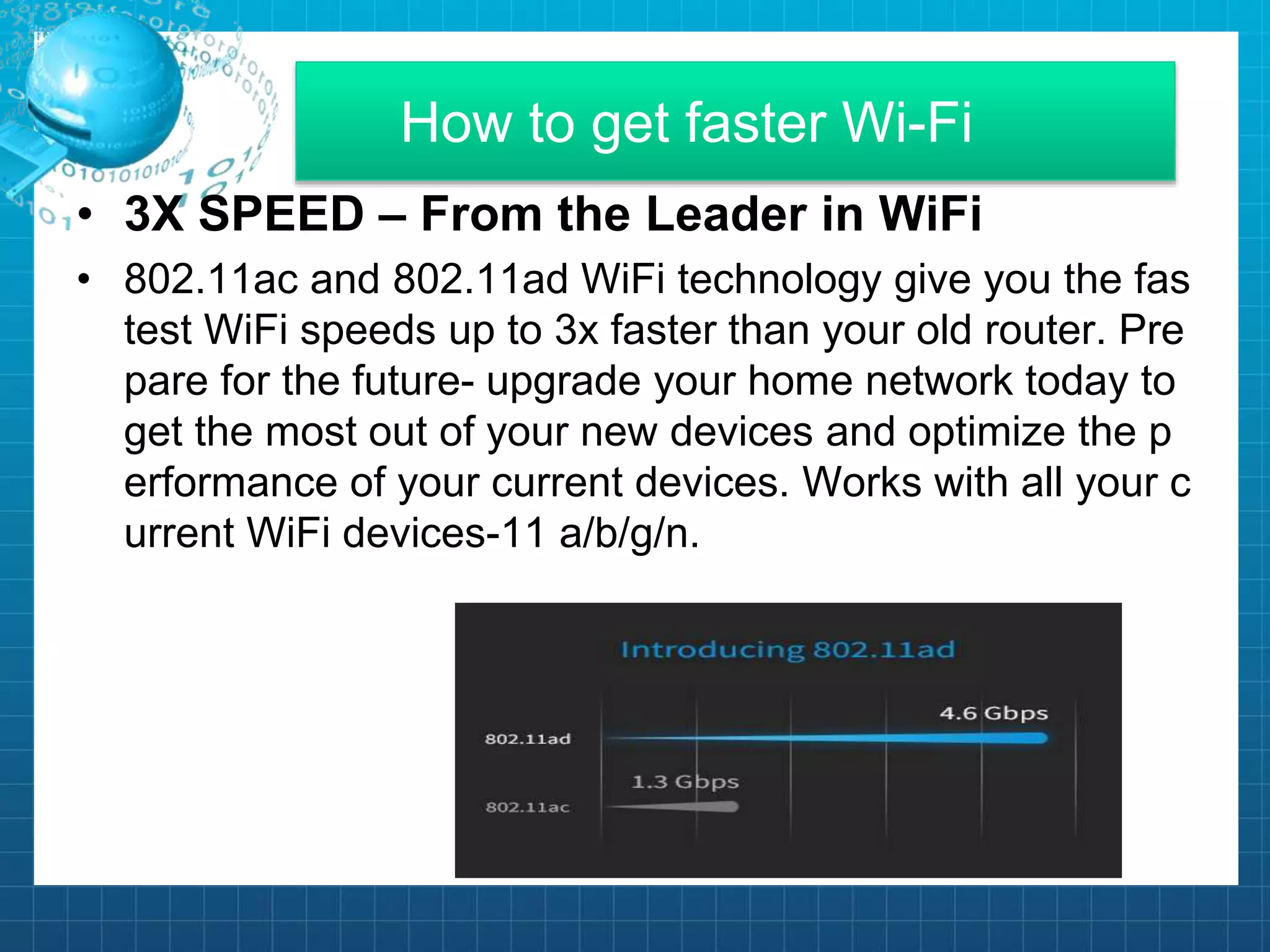
The document provides an overview of Wi-Fi technology. It discusses how Wi-Fi works using radio waves to create wireless hotspots for connecting devices. It outlines the advantages of Wi-Fi like mobility, ease of installation, and flexibility. It also describes the various IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standards including 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. Finally, it discusses how Wi-Fi is used in applications like wireless networks and Wi-Fi phones and how to get faster Wi-Fi speeds.