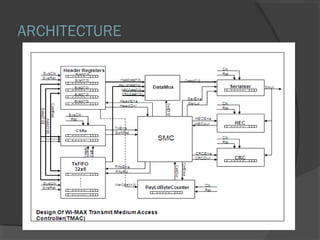
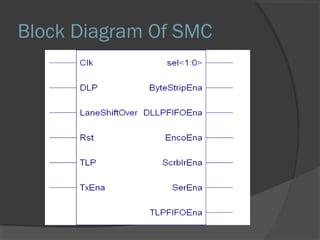
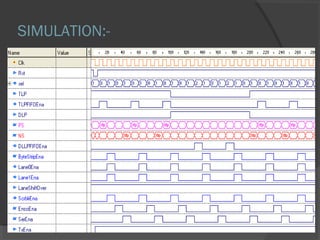
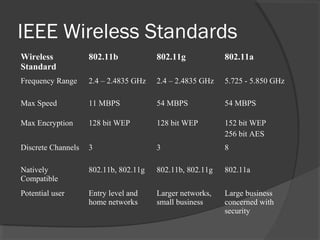
This document discusses Wi-Fi technology and its components. Wi-Fi allows wireless connectivity between devices using radio waves instead of wires. It uses IEEE 802.11 standards for wireless local area networks (WLANs). Key components of a Wi-Fi network include an access point connected to a wired internet connection, Wi-Fi cards or adapters in devices, and Wi-Fi configuration. Wi-Fi provides mobility, ease of installation, and flexibility but has limitations such as range and potential interference.