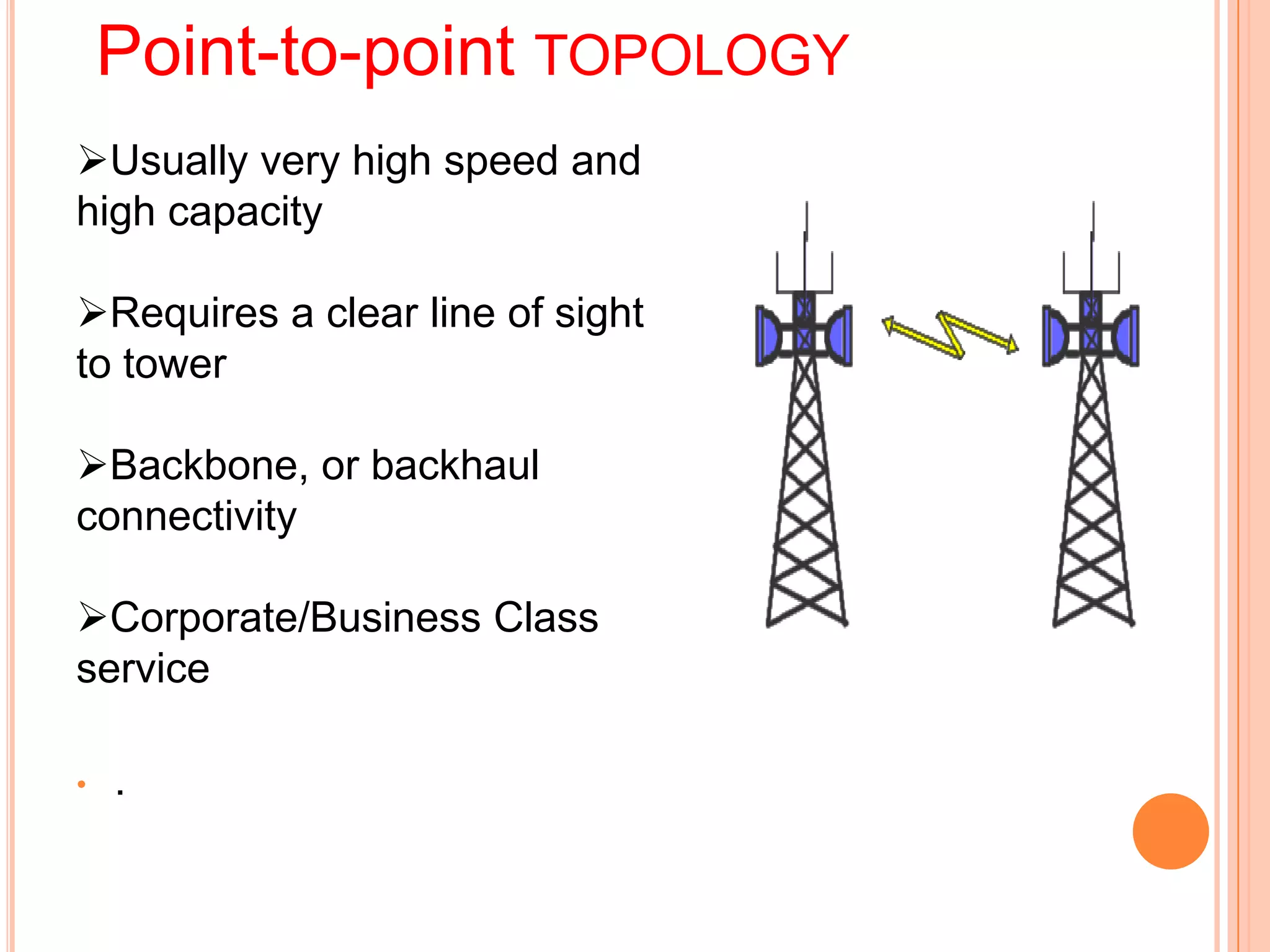
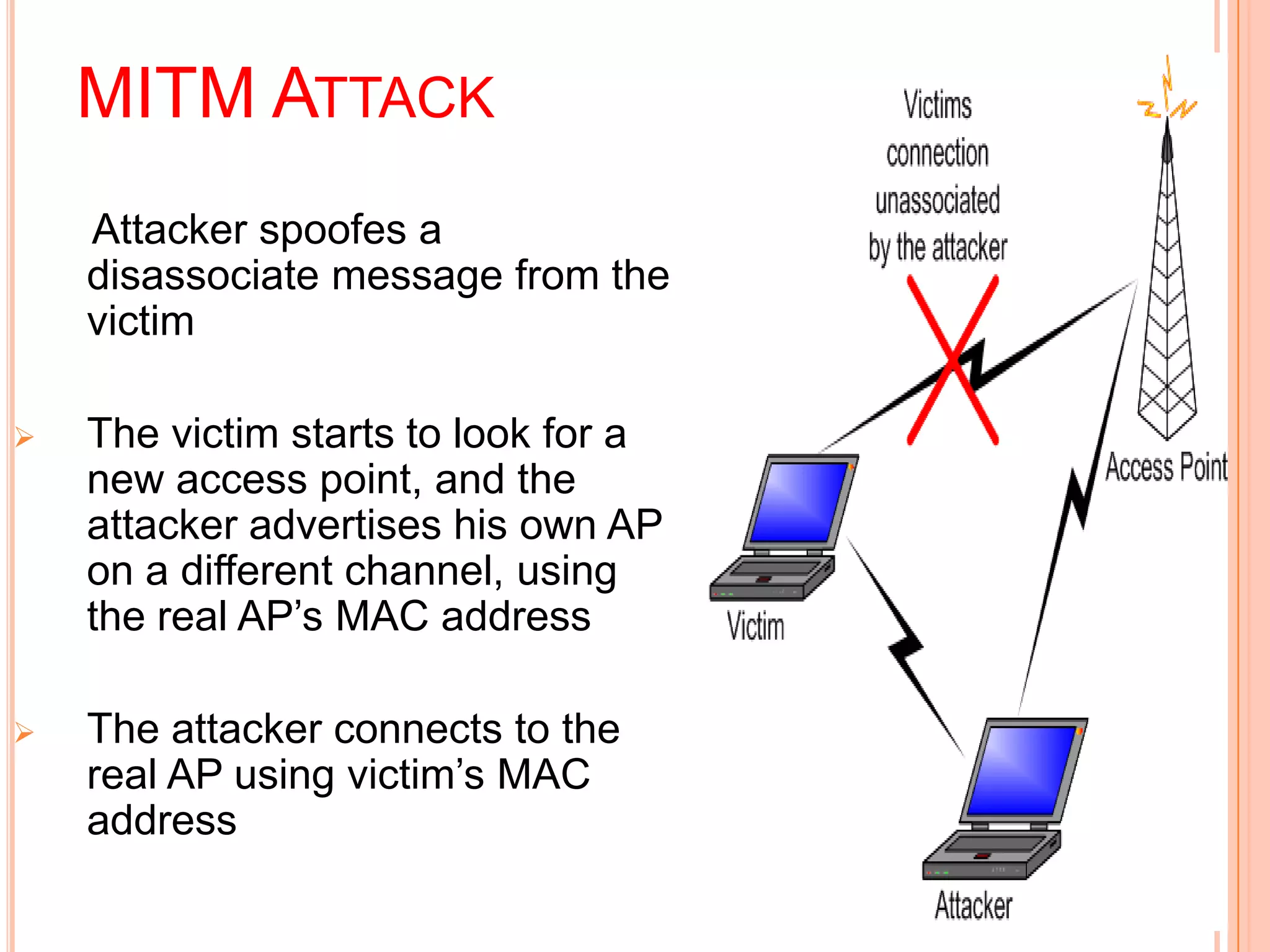
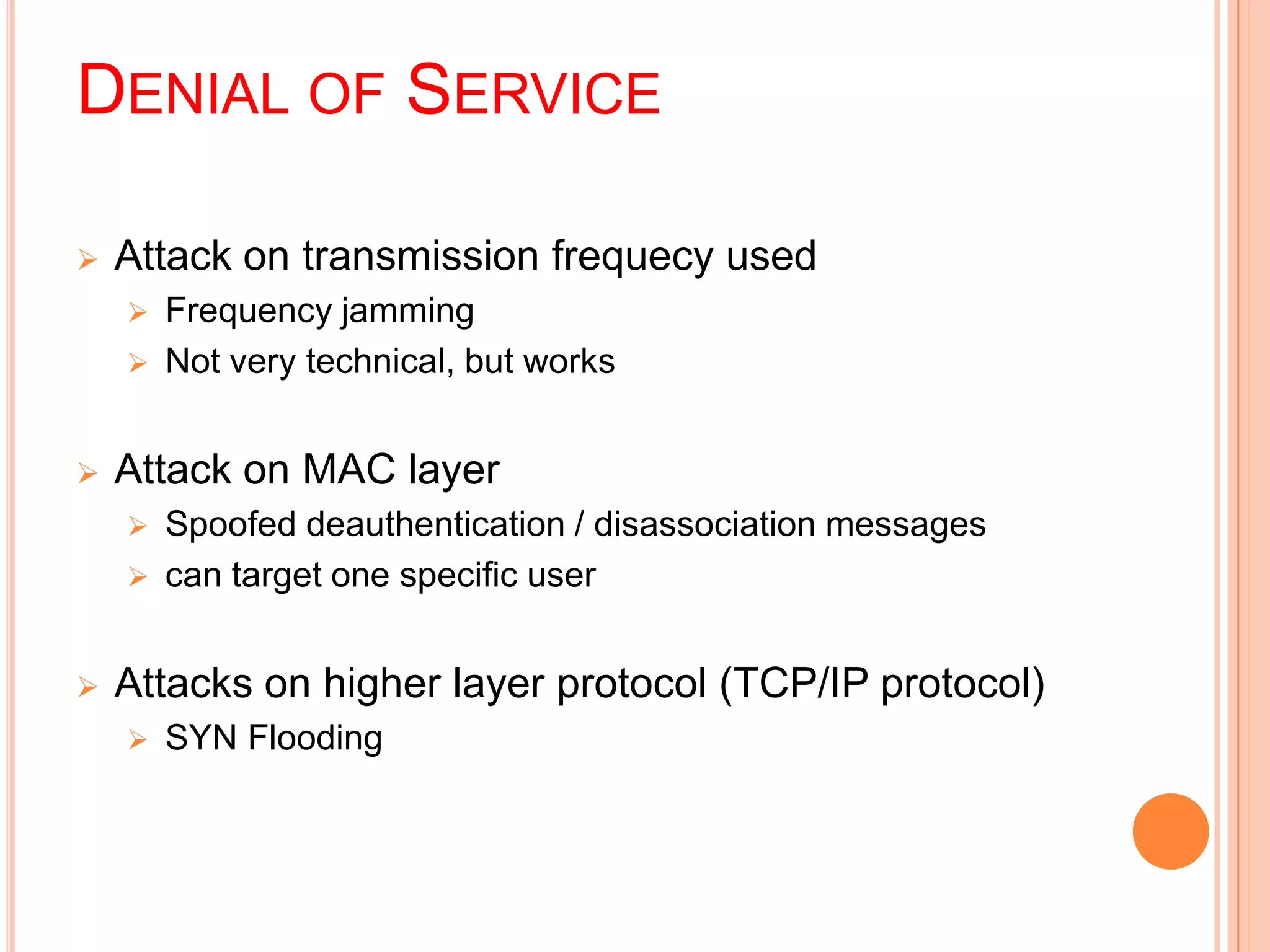
Wi-Fi, also known as wireless fidelity, allows devices to connect to the internet without cables. It uses radio waves to transmit and receive data between devices within range of a wireless access point. Common Wi-Fi standards include 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. A Wi-Fi network requires an access point connected to a wired network, wireless network cards or adapters in devices, and may include additional components like antennas, bridges, and firewalls for security. Wi-Fi provides mobility and flexibility but can experience interference issues and has a limited range compared to wired connections.