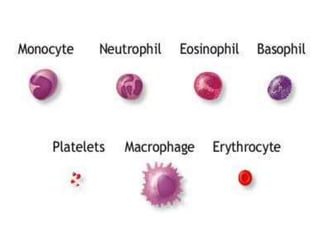
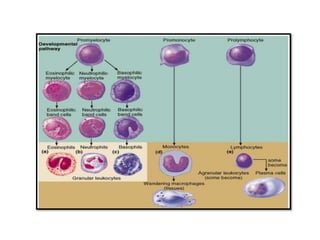
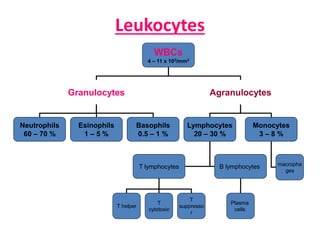
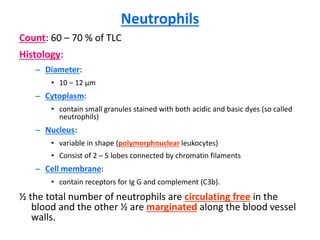
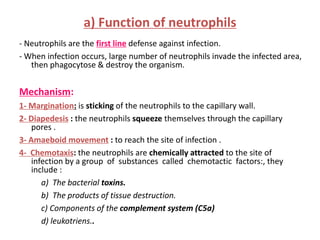
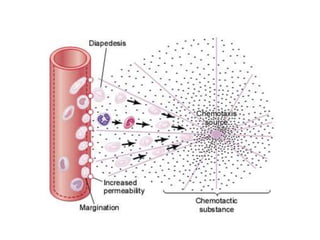
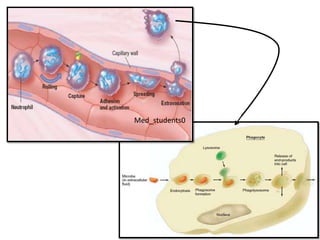
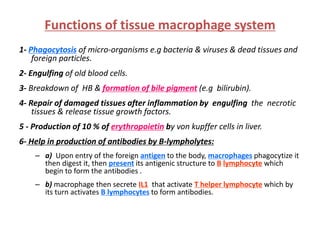
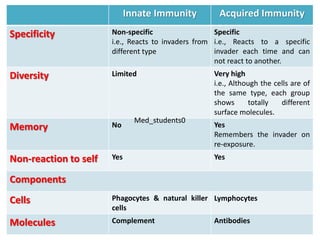
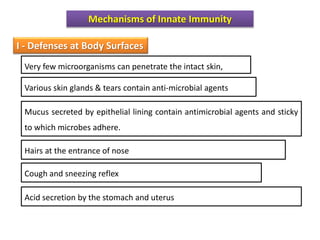
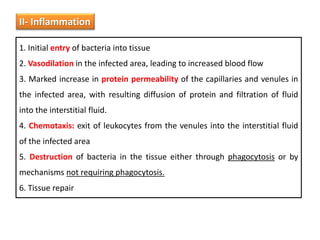
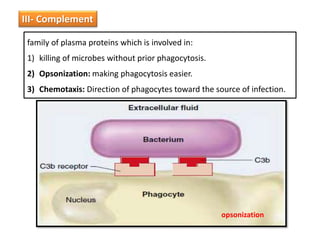
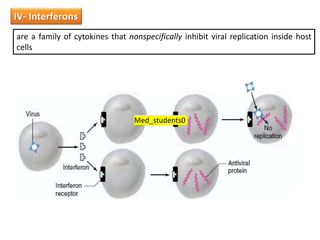
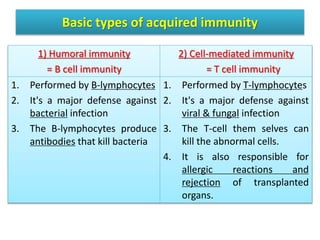
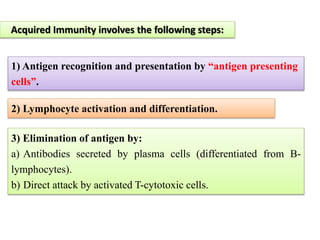
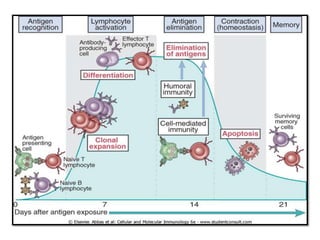
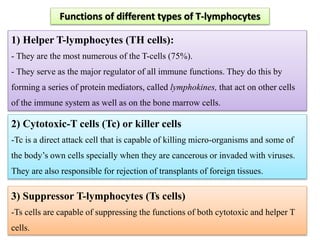
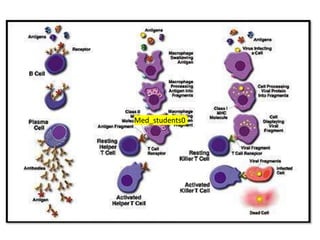
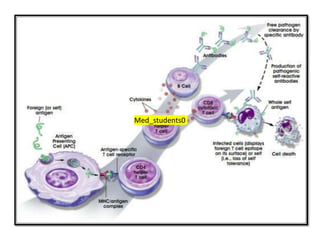
White blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes are the mobile units of the immune system that help protect the body from infection and disease. There are two main types of WBCs: granulocytes which have granules in their cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils; and agranulocytes which do not have granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes. Each type of WBC has a specific function such as phagocytosis, antibody production, or regulation of the immune response. Together, WBCs provide a powerful defense mechanism against infections, tumors, and toxins.