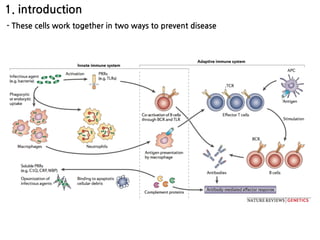
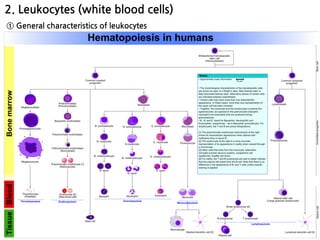
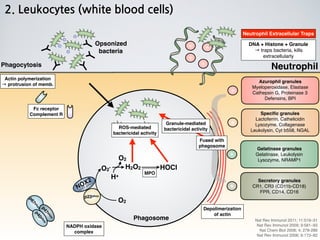
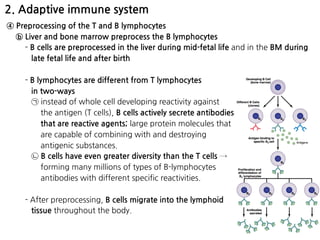
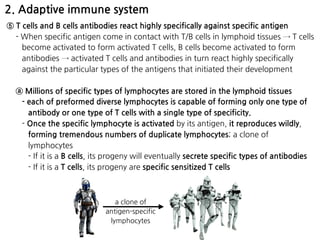
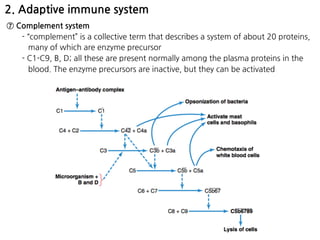
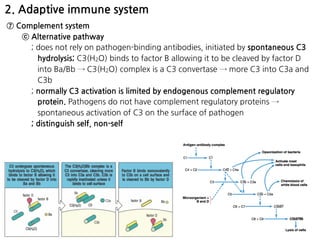
1. Leukocytes (white blood cells) play an important role in the body's immune defense against infection. They are divided into granulocytes like neutrophils and macrophages, which provide innate immunity through phagocytosis, and lymphocytes/plasma cells, which provide adaptive immunity.
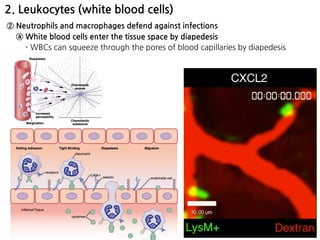
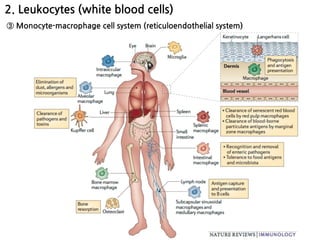
2. Neutrophils and macrophages are attracted to sites of infection by chemotaxis and enter tissues through diapedesis. They then phagocytose and destroy invading bacteria and viruses. Macrophages reside long-term in tissues as part of the monocyte-macrophage system.
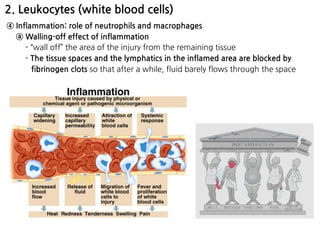
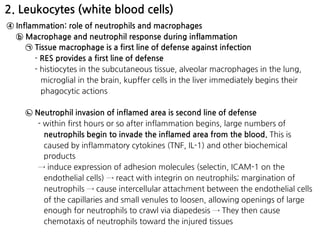
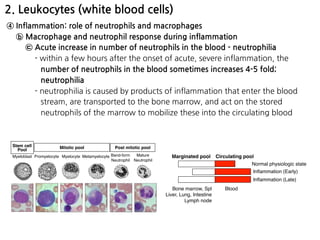
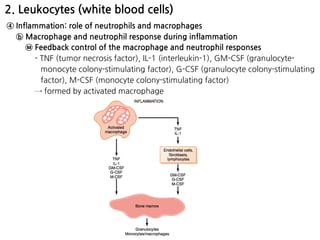
3. During inflammation, neutrophils and macrophages are the first and second lines of defense, respectively, migrating to the















































































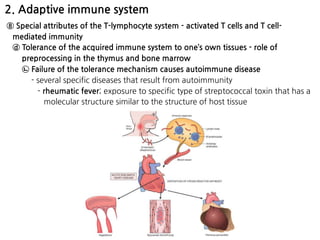


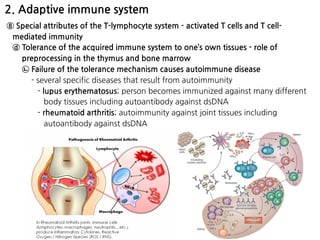






![Dendritic cells
- largerhans cells (discovered in late 19th century)
- the term “dendritic cells” were coined in 1973 by R. Steinman
- connect innate and adaptive immunity, professional APC
Name Description Secretion
Toll-like
receptors
Conventional dendritic cell
(previously called Myeloid dendritic
cell) (cDC or mDC)
Most similar to monocytes. mDC are
made up of at least two subsets:
(1) the more common mDC-1, which is a
major stimulator of T cells
(2) the extremely rare mDC-2, which may
have a function in fighting wound
Interleukin 12 (IL-12)
TLR 2, TLR
4
Plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC)
Look like plasma cells, but have certain
characteristics similar to myeloid
dendritic cells.[6]
Can produce high amounts of interferon-
alpha[7] and were previously called interferon-
producing cells.[8]
TLR 7, TLR
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-170726070318/85/slide-114-320.jpg)


