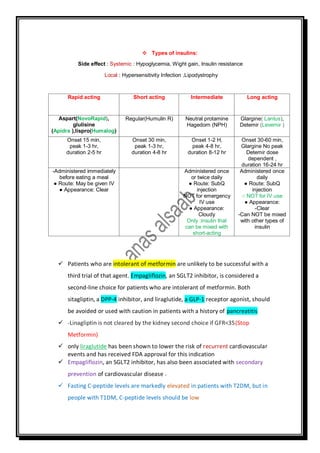
The document outlines various antidiabetic medications, detailing their mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and their impact on blood glucose levels. Key highlights include the recommendation to stop certain medications before IV contrast and their variances in safety during pregnancy, particularly with respect to categories and renal function. Additionally, it emphasizes specific choices for patients intolerant to metformin, as well as the cardiovascular benefits associated with liraglutide and empagliflozin.