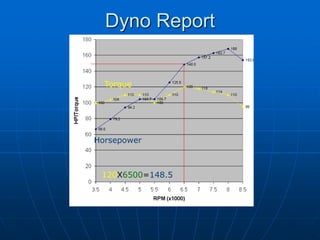
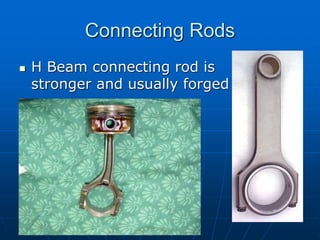
This document discusses ways to enhance engine performance through modifications to core components. It explains that increasing displacement through boring or using a stroker crank can boost torque. Using forged internals like connecting rods and a performance crank shaft, as well as high-lift cams and roller rockers, allows for more power. Porting the heads and using equal-length headers improves airflow. Balancing and blue printing the assembled engine ensures optimal performance.