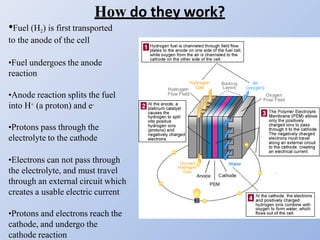
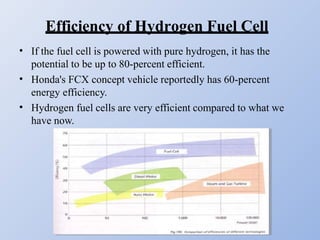
Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen without combustion. They have various applications including powering vehicles, electronics, and buildings. Some advantages are that they do not produce emissions and can use hydrogen produced from renewable sources. However, challenges remain regarding producing, storing, and transporting hydrogen fuel as well as the high costs of fuel cells and catalysts. Future development aims to address these issues and expand hydrogen's role in energy systems through increasing infrastructure and reducing costs.