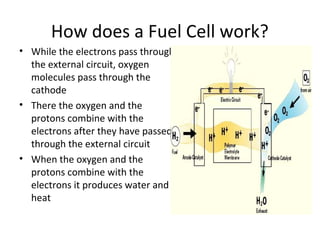
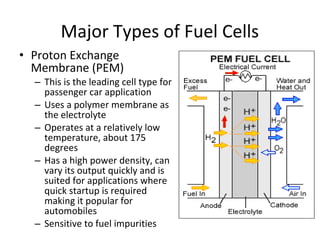
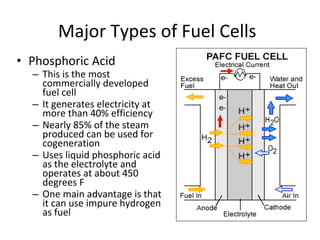
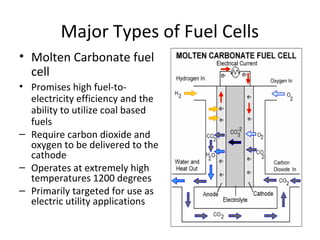
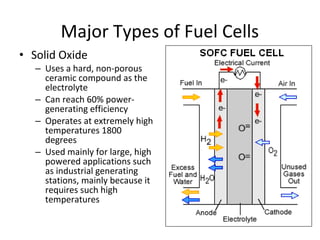
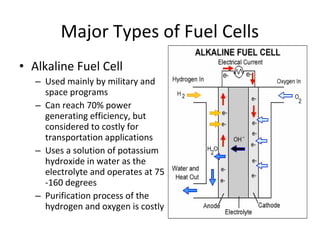
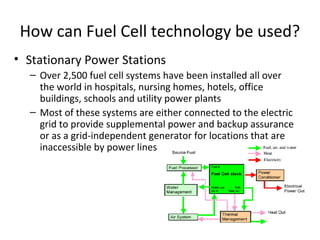
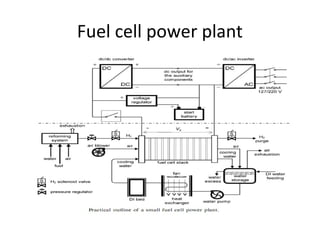
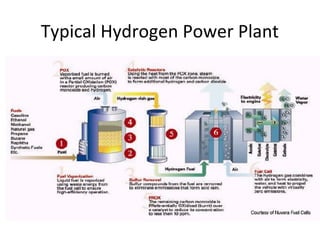
The document discusses fuel cells as electrochemical devices that generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, with water and heat as byproducts. It outlines the importance of fuel cell technology in providing clean, efficient energy compared to traditional combustion methods and details various types of fuel cells, their efficiencies, and applications in transportation, stationary power, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. Additionally, the document highlights challenges in hydrogen production and storage that need to be addressed for widespread fuel cell adoption.