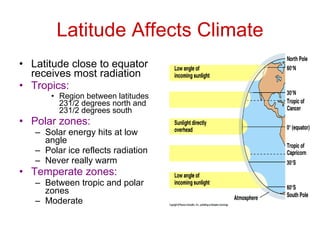
Climate is determined by averaging weather over a long period of time, at least 30 years. Several factors affect a region's climate, including latitude, topography, oceans and lakes, and ocean currents. Latitude affects climate the most - regions close to the equator receive the most solar radiation and have tropical climates, while polar zones receive energy at a low angle and have polar climates. Between the tropics and polar zones are temperate zones with more moderate climates. Topography like large bodies of water and mountains also influence climate by changing temperature, moisture, and wind patterns in coastal and mountainous regions. Large cities can create "heat islands" and change local wind and precipitation patterns compared to surrounding areas.