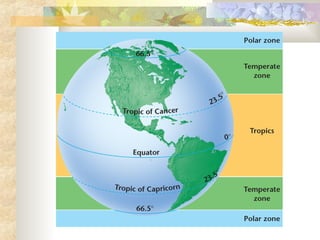
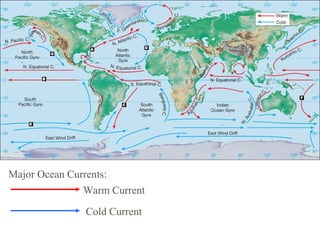
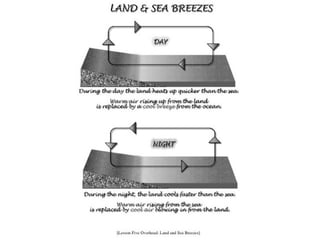
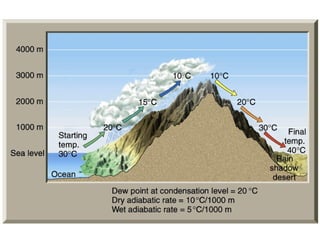
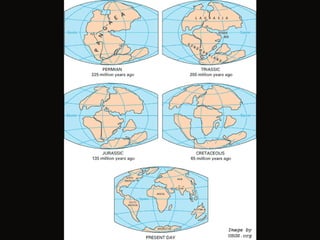
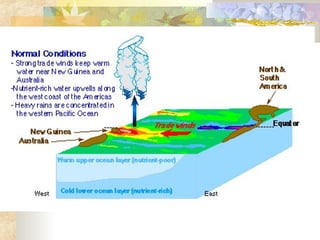
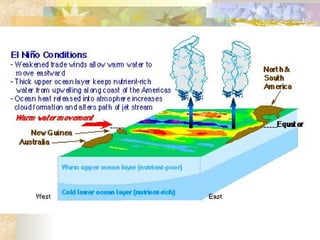
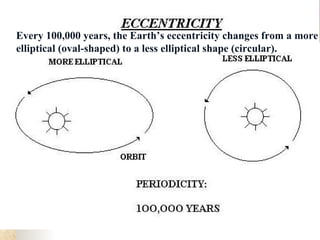
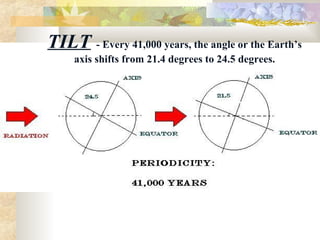
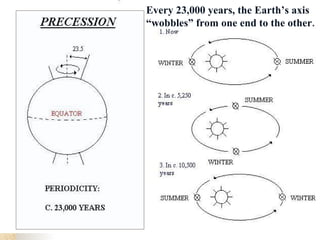
Climate is determined by temperature and precipitation patterns over long periods of time. Several factors influence climate, including latitude, elevation, ocean currents, prevailing winds, and mountain ranges. Climates are generally divided into polar, temperate, and tropical zones based on average temperatures. The climate changes naturally over long timescales due to drifting continents, variations in the sun's output, and periodic changes in the Earth's orientation and orbit known as the Milankovitch cycles, which have corresponded with ice ages in the past. Human activities like burning fossil fuels may also impact climate by increasing greenhouse gas levels and global temperatures.