Embed presentation
Downloaded 49 times





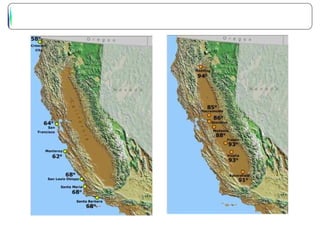
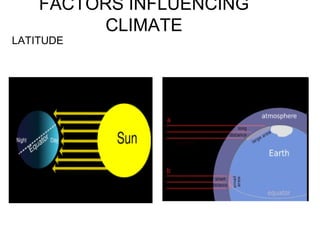
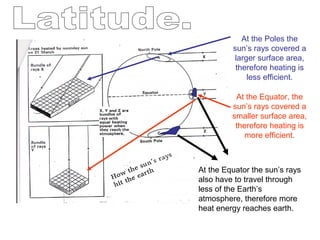
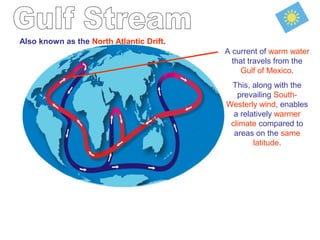
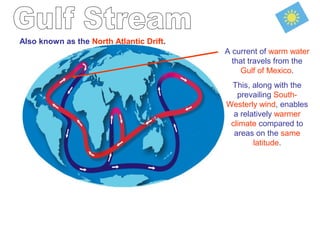

The document discusses several factors that influence climate such as latitude, elevation, proximity to bodies of water, and ocean currents. Places closer to the equator experience more direct sunlight which allows for more efficient heating. Higher elevations experience lower temperatures with each increase in altitude. Bodies of water moderate temperatures since water heats and cools more slowly than land. Ocean currents also impact climate by transporting warm or cold water to landmasses.









