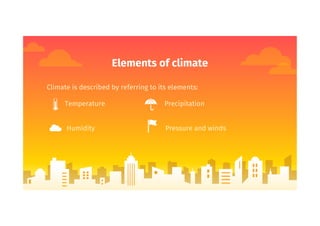
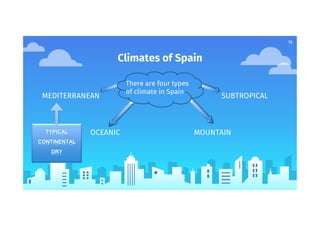
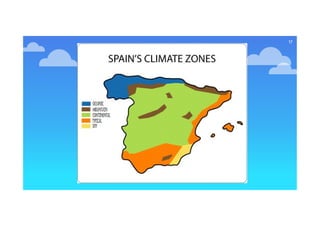
Climate refers to average atmospheric conditions over a long period of time, usually 30-35 years, while weather describes short term conditions. The document then discusses key climate elements - temperature, humidity, precipitation, pressure and winds - and how they are influenced by factors like latitude, altitude, and distance from the sea. Coastal areas generally have milder winters and cooler summers than inland areas. Spain has four main climate types - Mediterranean, Continental, Oceanic and Mountain - which are described based on their characteristic temperatures and precipitation patterns.