The document provides an overview of key concepts in wave phenomena. It defines waves as oscillations generated by vibrating systems. Wave fronts connect particles moving in the same phase and are perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to propagation, while longitudinal waves oscillate parallel. Amplitude is the maximum displacement from equilibrium, period is time for one oscillation, and frequency is oscillations per second. Waves can be described graphically and using the wave equation relating velocity, frequency, and wavelength. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference are described for water and sound waves, as well as electromagnetic waves.
![Hoo Sze Yen www.physicsrox.com Physics SPM 2012
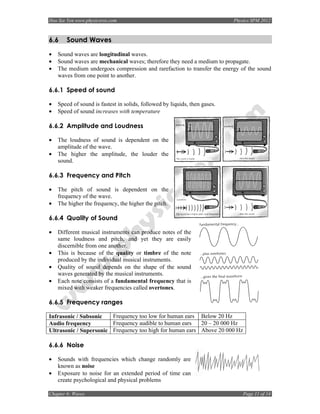
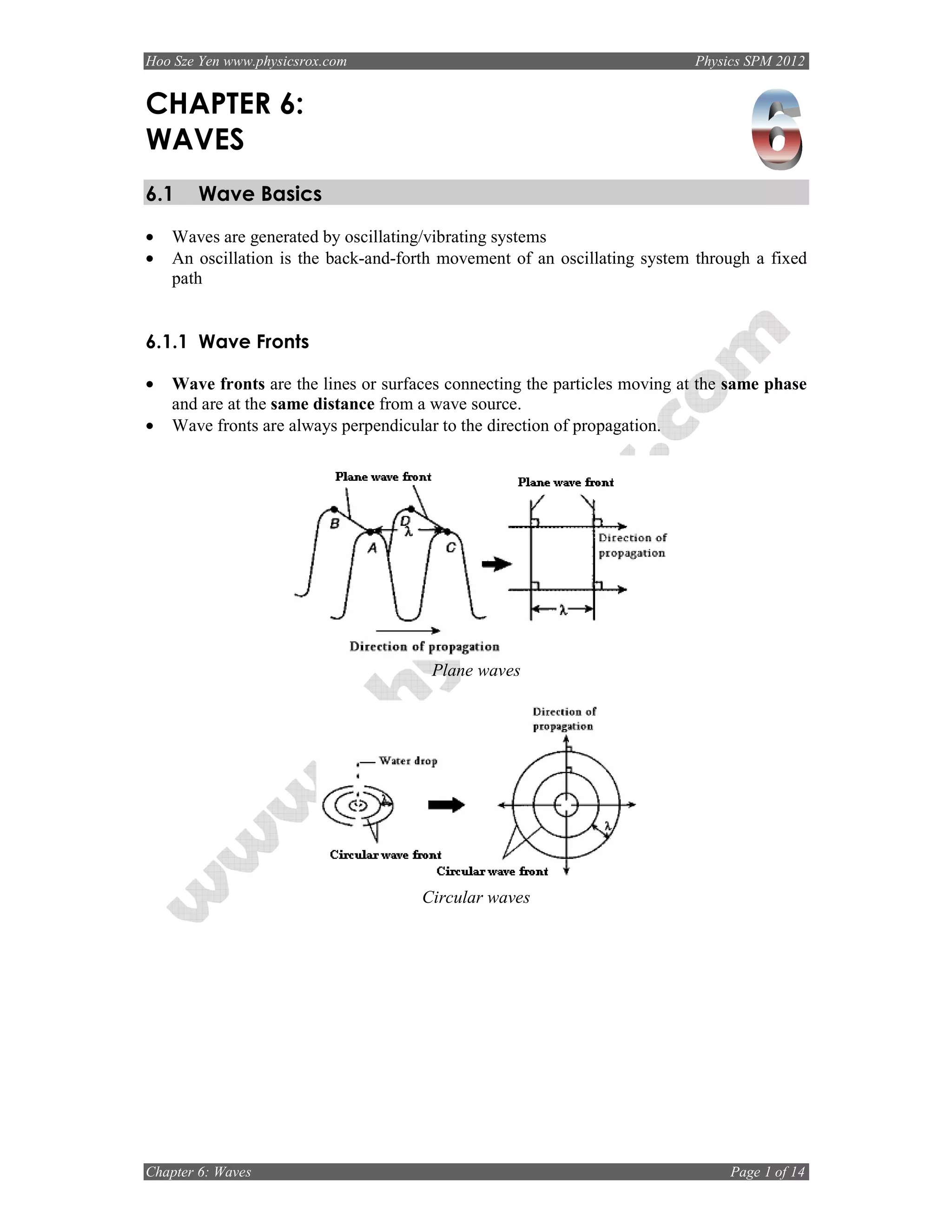
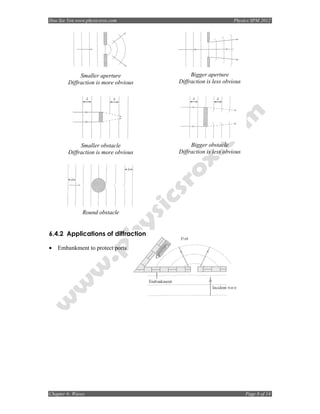
6.1.2 Types of Waves
Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves
Transverse waves are waves which oscillate Longitudinal waves are waves which
perpendicular to the direction of oscillate parallel to the direction of
propagation. propagation.
E.g: Light waves E.g: Sound waves
6.1.3 Amplitude, Period and Frequency
• Amplitude is the maximum displacement of an object from its equilibrium position [m]
• Period is the time taken for a particle to make one complete oscillation [s]
time taken
Period, T =
number of oscillatio ns
• Frequency is the number of complete oscillations in one second [Hz]
number of oscillations
Frequency, f =
time taken
1
f =
T
Chapter 6: Waves Page 2 of 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-6-waves-2012-120912084359-phpapp01/85/Chapter-6-waves-2012-2-320.jpg)
![Hoo Sze Yen www.physicsrox.com Physics SPM 2012
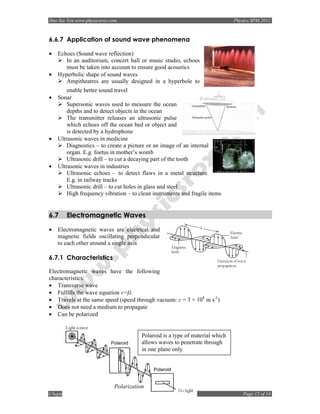
6.1.4 Graphs
Displacement-time graph
Amplitude
Amplitude
Displacement-distance graph
6.1.5 Wave Equation
v = fλ
where v = velocity of the wave [m s-1]
f = frequency of the wave [Hz]
λ = wavelength [m]
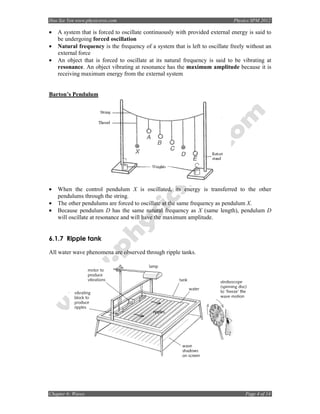
6.1.6 Damping and Resonance
• An oscillating system which has a reducing amplitude over time is said to be undergoing
damping. Damping is due to lost energy through friction and heat.
External damping: Loss of heat energy because of friction with the air
Internal damping: Loss of heat energy because of the compression and tension of the
molecules in the system
Chapter 6: Waves Page 3 of 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-6-waves-2012-120912084359-phpapp01/85/Chapter-6-waves-2012-3-320.jpg)

![Hoo Sze Yen www.physicsrox.com Physics SPM 2012
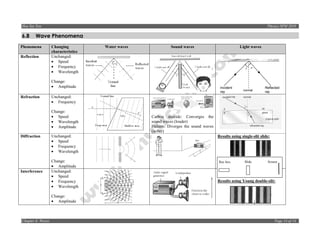
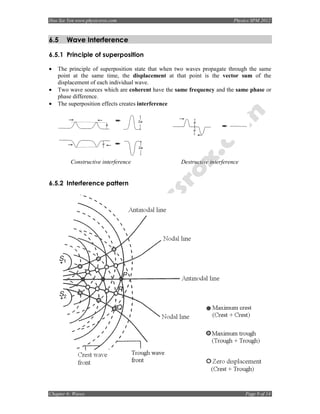
6.5.3 Interference equation
ax
λ=
D
where λ = wavelength [m]
a = distance between sources [m]
x = distance between two successive antinodal/nodal lines [m]
D = distance between a and x [m]
6.5.4 Different frequencies
Low frequency High frequency
(large wavelength) (small wavelength)
Value of x is larger Value of x is smaller
6.5.5 Different distance between the sources
Larger distance between the sources Smaller distance between the sources
Value of x is smaller Value of x is larger
Chapter 6: Waves Page 10 of 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-6-waves-2012-120912084359-phpapp01/85/Chapter-6-waves-2012-10-320.jpg)