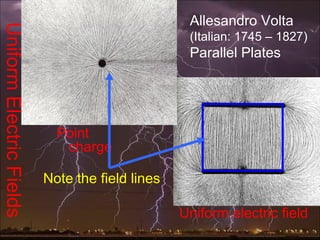
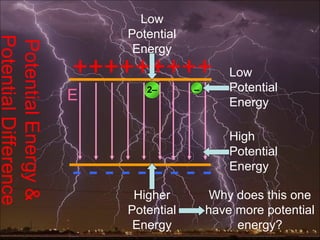
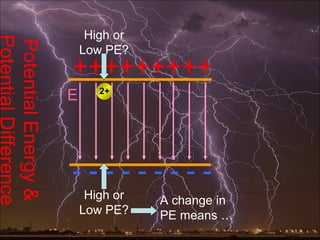
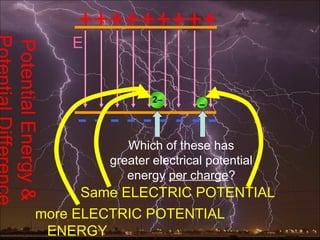
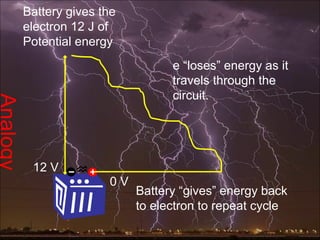
Electric potential energy and gravitational potential energy both increase as work is done to overcome a field and raise an object or charge. Voltage measures electric potential energy per unit charge and represents how much energy a charge will gain or lose when moving through a potential difference. It is defined as the change in electric potential energy divided by the charge and can be measured in joules per coulomb (volts).