This document discusses electrostatics and charge. It contains the following key points:
1. Charge is an inherent property of matter that comes in two types: positive and negative. Protons and electrons have equal but opposite charges.
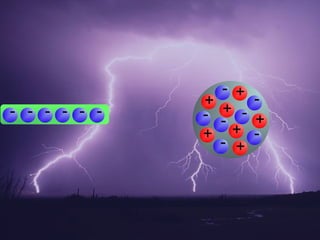
2. The net electric charge of a system must remain constant according to the law of conservation of charge. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
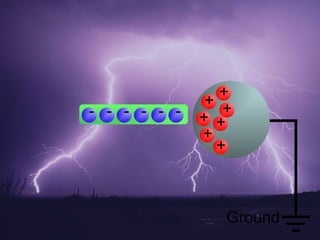
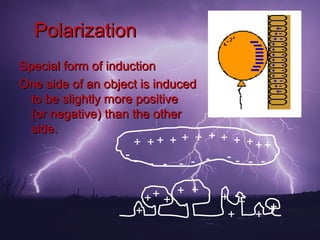
3. There are three ways to charge an object: through friction, contact, or induction. Grounding encourages charges to flow to a neutral object like the earth. Polarization is a special form of induction where one side of an object becomes slightly more positive or negative.