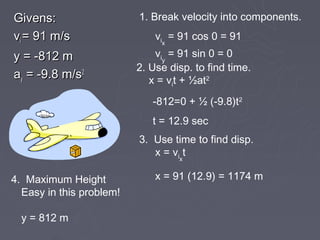
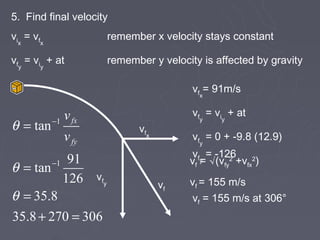
1) The document describes the components and steps for solving 2-dimensional projectile motion problems.
2) It explains that projectile motion problems can be broken into independent horizontal and vertical components using velocity and acceleration.
3) The document provides the key steps to solve all 2D projectile motion problems: (1) break velocity into x and y components, (2) use displacement to find time, (3) use time to find other displacement, (4) find maximum height, and (5) find final velocity.
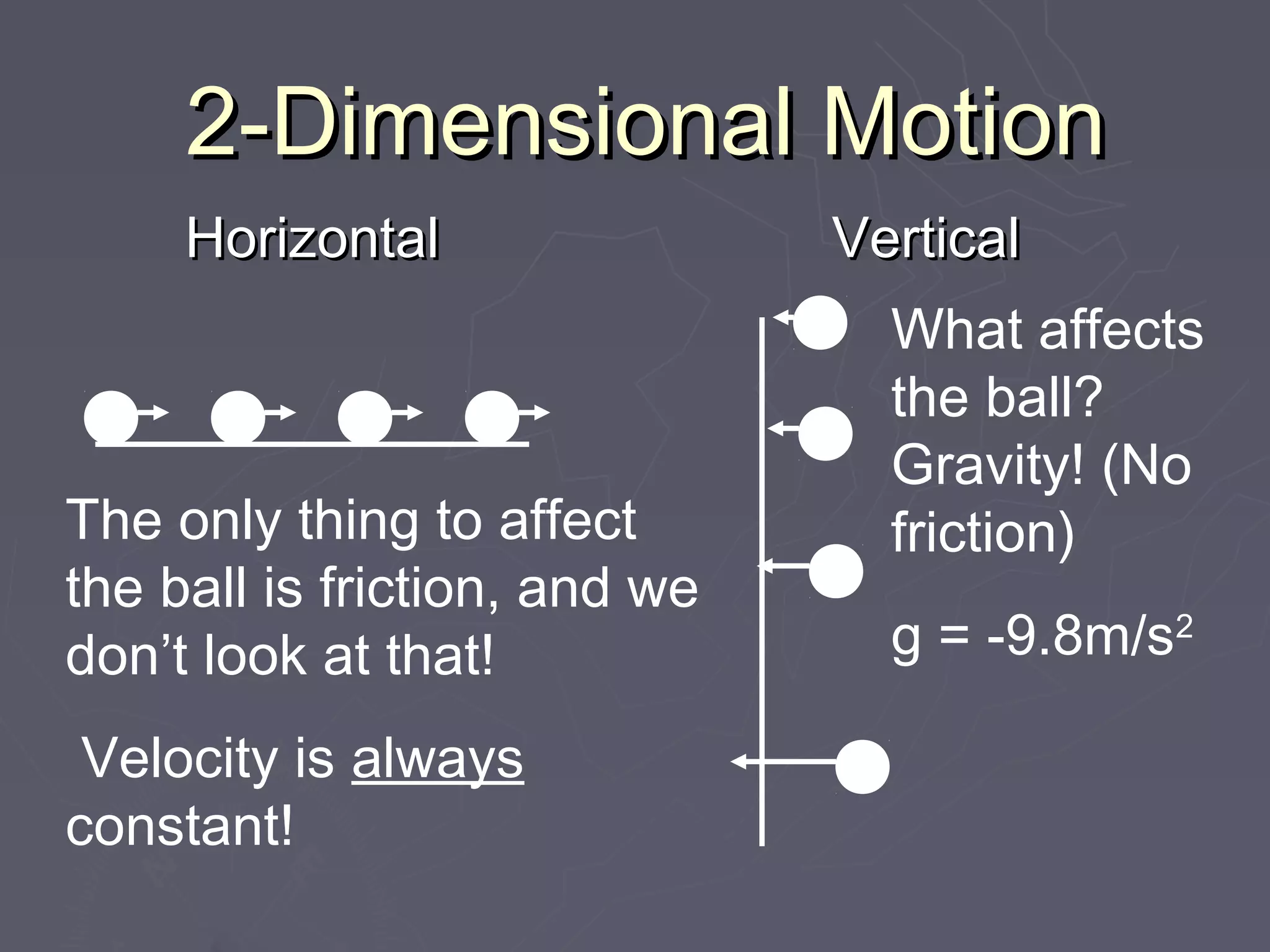
![Combine Horizontal and Vertical
components are independent!
the two (They don’t affect each
other. It doesn’t matter how
fast the object is going in the
x direction, gravity still acts
evenly on the object.) [Quarters]
So … all these problems are at
least 2 steps: one step in the y
direction, one step in the x
direction.
time is what combines the two.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-2-dkinematicsnotes-120830125848-phpapp01/85/2-2-d-kinematics-notes-2-320.jpg)