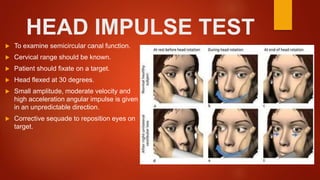
The document provides detailed information on the anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system, including its components such as the cochlea, semicircular canals, and receptors. It describes key functions like equilibrium maintenance and sensory processing, along with physical tests like the caloric test, dizziness handicap inventory, and head impulse test used to assess vestibular function. Each test's methodology and purpose are outlined, highlighting their relevance in diagnosing vestibular disorders.