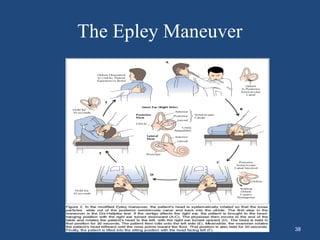
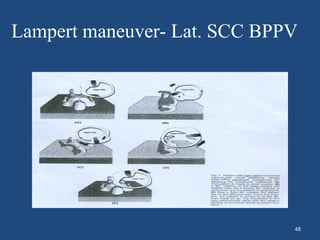
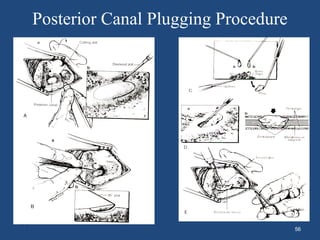
This document discusses benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). It begins with an overview of the anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. It then defines BPPV and discusses its pathogenesis, symptoms, types, differential diagnosis, investigations and treatment modalities. The most common treatment is canalith repositioning procedures like the Epley maneuver which aims to move otoliths out of the semicircular canals.