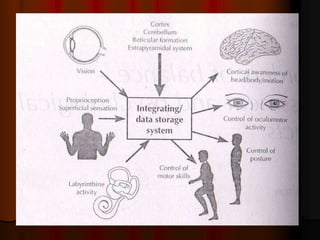
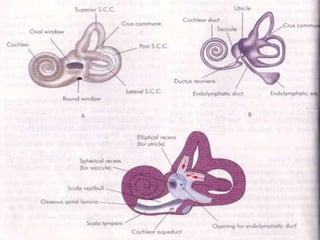
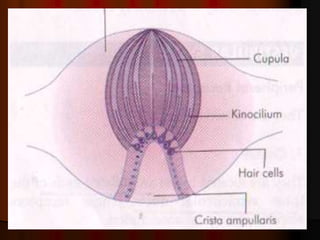
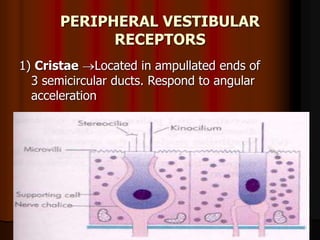
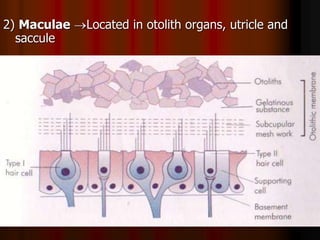
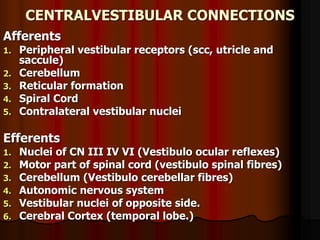
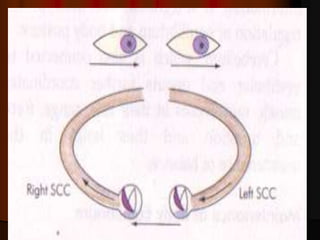
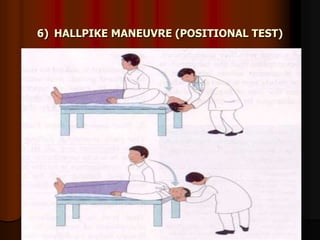
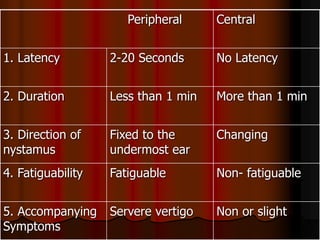
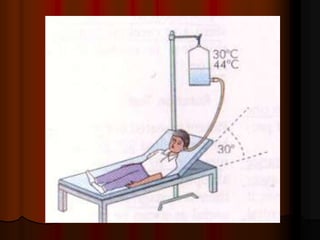
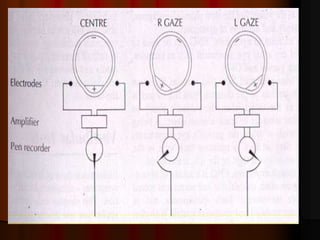
This document discusses tests used to assess vestibular function, including both clinical tests and laboratory tests. It first provides an overview of anatomy related to the vestibular system. It then describes various clinical tests such as spontaneous nystagmus, fistula tests, Romberg tests, and gait analysis. Laboratory tests discussed include caloric testing, electronystagmography, optokinetic testing, rotation testing, and galvanic testing. The goal of these tests is to evaluate the vestibular system both peripherally and centrally in order to diagnose causes of dizziness and imbalance.