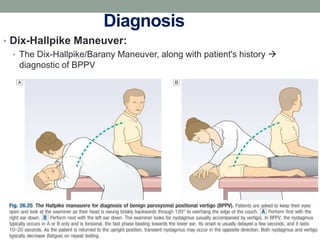
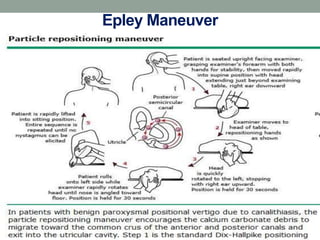
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is the most common cause of positional vertigo, primarily affecting women, often due to displaced otolithic debris in the semicircular canals. Symptoms include sudden episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements, with diagnosis typically confirmed through the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. Management options include the Epley maneuver for particle repositioning, various medications, and surgical interventions if necessary.