Vectorization is the process of converting words into numerical representations. Common techniques include bag-of-words which counts word frequencies, and TF-IDF which weights words based on frequency and importance. Word embedding techniques like Word2Vec and GloVe generate vector representations of words that encode semantic and syntactic relationships. Word2Vec uses the CBOW and Skip-gram models to predict words from contexts to learn embeddings, while GloVe uses global word co-occurrence statistics from a corpus. These pre-trained word embeddings can then be used for downstream NLP tasks.













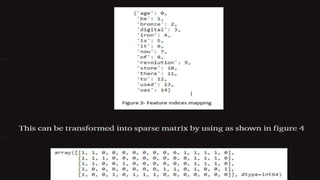
![So here we basically convert word into vector .
By following same approach other vector value are as follow:
“There used to be bronze age” = [1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0]
“There used to be iron age” = [1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0]
“There was age of revolution” = [1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0]
“Now its digital Age” = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectorizationinnlp-230614120845-fcc9aa08/85/Vectorization-In-NLP-pptx-16-320.jpg)