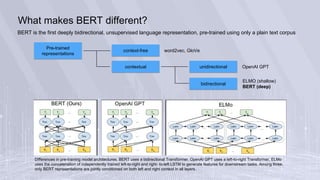
BERT is a deeply bidirectional, unsupervised language representation model pre-trained using only plain text. It is the first model to use a bidirectional Transformer for pre-training. BERT learns representations from both left and right contexts within text, unlike previous models like ELMo which use independently trained left-to-right and right-to-left LSTMs. BERT was pre-trained on two large text corpora using masked language modeling and next sentence prediction tasks. It establishes new state-of-the-art results on a wide range of natural language understanding benchmarks.



![BERT (2/4)
• Pre-training tasks
– Masked language model
• 80% of the time: Replace the word with the [MASK] token, e.g., my dog is hairy → my dog is [MASK]
• 10% of the time: Replace the word with a random word, e.g., my dog is hairy → my dog is apple
• 10% of the time: Keep the word un- changed, e.g., my dog is hairy → my dog is hairy
– Next sentence prediction
• Input = [CLS] the man went to [MASK] store [SEP] he bought a gallon [MASK] milk [SEP]
Label = IsNext
• Input = [CLS] the man [MASK] to the store [SEP] penguin [MASK] are flight ##less birds [SEP]
Label = NotNext
• Pre-training procedure
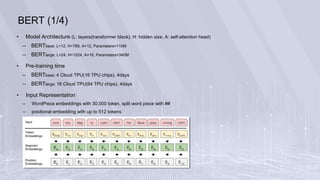
– BooksCorpus(800M words) & English Wikipedia(2,500M words)
– sentence A embedding + sentence B embedding(50% is actual next, 50% is random), combined length <= 512
tokens
– batch size: 256 sequence * 512 tokens = 128,000 tokens/batch for 1M steps, 40 epochs over 3.3B word corpus
– Adam, dropout (0.1 on all layers), ‘gelu’ activation (=OpenAI GPT)
– training loss = mean MLM likelihood + mean next sentence prediction likelihood](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bertintroduction-181119081439/85/BERT-introduction-6-320.jpg)
![BERT (3/4)
• Fine-tuning procedure
– batch size: 16, 32
– Learning rate(Adam): 5e-5, 3e-5, 2e-5
– epochs: 3,4
• BERT vs OpenAI GPT
– OpenAI GPT: left-to-right Transformer LM on a large text corpus
GPT BERT
BooksCorpus (800M words) BooksCorpus (800M words) and Wikipedia (2,500M words)
sentence separator ([SEP]) and classifier token ([CLS]) which
are only introduced at fine-tuning time
learns [SEP], [CLS] and sentence A/B embed- dings during
pre-training
1M steps with a batch size of 32,000 words 1M steps with a batch size of 128,000 words
same learning rate of 5e-5 for all fine-tuning experiments
task-specific fine-tuning learning rate which performs the best
on the development set](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bertintroduction-181119081439/85/BERT-introduction-7-320.jpg)

